
Differences between pharynx and larynx
S.N. Pharynx Larynx 1. It is located at the back of buccal cavity. It is located in the upper part of the neck. 2. It […]

S.N. Pharynx Larynx 1. It is located at the back of buccal cavity. It is located in the upper part of the neck. 2. It […]

S.N. Glycogen Starch 1. It is the main reserve food material of animal cells, hence also called animal starch. It is the main reserve food […]
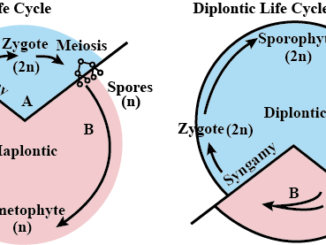
S.N. Diplontic life cycle Haplontic life cycle 1. It occurs in higher organisms, many protozoans and some lower plants. It occurs in fungi, certain […]
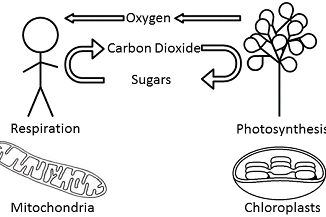
S.N. Photosynthesis Respiration 1. It is an anabolic process in which simple inorganic substances react to synthesize complex organic food. It is a catabolic process […]
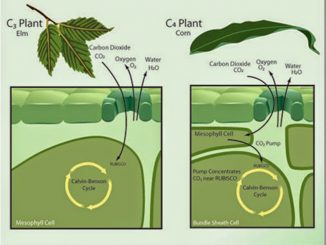
S.N. Calvin cycle (C3 cycle) Hatch and Slack cycle (C4 cycle) 1. The primary acceptor of CO2 is a 5-carbon compound, Ribulose-1, 5- biphosphate. The […]
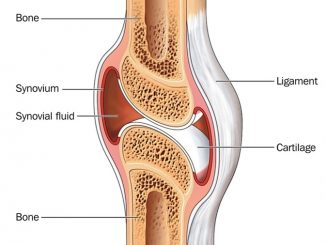
S.N. Bone Cartilage 1. Matrix is composed of a tough, inflexible material, the ossein. Matrix is composed of a firm, but flexible material, the chondrin. […]
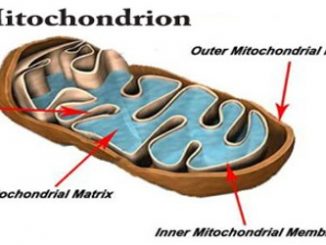
S.N. Outer mitochondrial membrane Inner mitochondrial membrane 1. It is smooth, having much less surface area. It is unfolded to form cristae, hence having […]
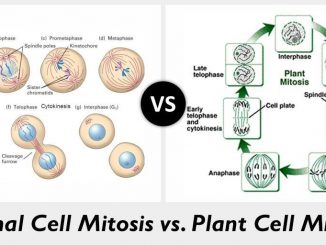
S.N. Mitosis in Animal cells Mitosis in Plant cells 1. Centrioles are present at the spindle poles. Centrioles are lacking at the spindle poles. […]

S.N. Hare (Lepus) Rabbit (Oryctolagus) 1. It is a normad, staying temporarily at some sheltered spot behind a stone or under a bush. It […]

S.N. Hormones Enzymes 1. Hormones may be amino acid derivatives, peptides, proteins or steroids in nature. All enzymes are complex proteins. 2. They have low […]
Copyright © 2025 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes