| S.N. | Euchromatin | Heterochromatin |
| 1. | It consists of thin and extended chromatin fibers. | It consists of thick and compact chromatin fibers. |
| 2. | Chromatin fibers are uncoiled and scattered in the nucleoplasm. | Nucleoplasm consists of coiled and localized chromatin fibers. |
| 3. | It is found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. | It is found in eukaryotes only. |
| 4. | It forms the bulk of the chromatin. | It forms a fraction of chromatin. |
| 5. | It occupies most of the nucleus. | It lies close to the nuclear lamina. |
| 6. | It cannot be dyed completely, hence stains lightly. | It takes much color during staining and hence stains deeply or darkly. |
| 7. | Its genes are comparatively more active. | Its genes are less active or inactive. |
| 8. | The genes are transcribed. | The genes are not transcribed. |
| 9. | The replication of euchromatin occurs early in S-phase. | Its replicates late in S-phase. |
| 10. | It permits crossing over. | it doesn’t let crossing over occur in its genes. |
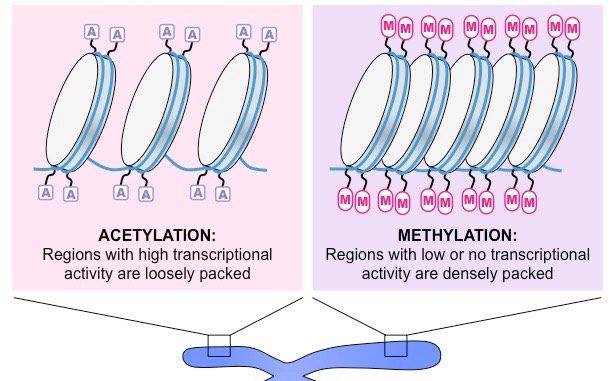
| 11. | The regions are acetylated. | The regions are methylated. |