
Differences between Agnatha and Gnathostomata
S.N. Agnatha Gnathostomata 1. Mouth is circular without jaws. Mouth is provided with jaws. 2. Paired appendages are lacking. Paired appendages are present, may be […]

S.N. Agnatha Gnathostomata 1. Mouth is circular without jaws. Mouth is provided with jaws. 2. Paired appendages are lacking. Paired appendages are present, may be […]

S.N. Male Ascaris Female Ascaris 1. Body is about 15-30 cm long. They are longer (20-40 cm) than males. 2. Their body is narrower. Their […]

S.N. Red Muscle Fibers White Muscle Fibers 1. They are dark red with abundant pigment, myoglobin. They are light in color as they have very […]

S.N. Mitochondria Chloroplasts 1. They are smaller in size (1-4 µm). They are bigger in size (4-10 µm). 2. They occur in practically all eukaryotic […]
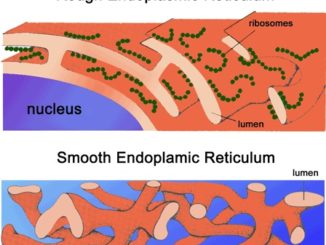
S.N. RER (Rough ER) SER (Smooth ER) 1. It is composed mainly of cisternae. It is composed mainly of tubules and vesicles. 2. It bears […]

S.N. Characteristics 70S Ribosomes 80S Ribosomes 1. Occurrence They occur in prokaryotic cells and in the mitochondria and plastids of eukaryotic cells. They occur only […]

S.N. Self-pollination Cross-pollination 1. Transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of the same flower (typical self-pollination) or another flower of the same […]
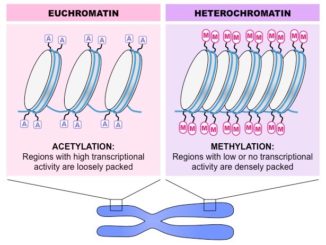
S.N. Euchromatin Heterochromatin 1. It consists of thin and extended chromatin fibers. It consists of thick and compact chromatin fibers. 2. Chromatin fibers are uncoiled […]
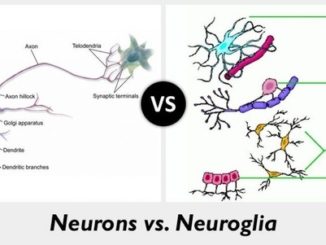
S.N. Nerve cells Glial cells 1. They are neuronal cells and are also called neurons. They are non-neuronal cells and are also called neuroglia. 2. […]
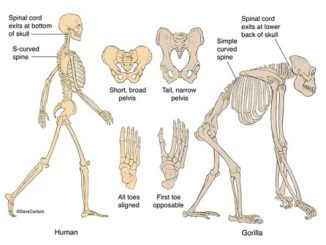
S.N. Man Apes 1. Mostly lead terrestrial life Chiefly lead arboreal life (except gorilla) 2. Walks in fully erect posture after infancy on the […]
Copyright © 2026 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes