
Differences between Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
S.N. Mitochondria Chloroplasts 1. They are smaller in size (1-4 µm). They are bigger in size (4-10 µm). 2. They occur in practically all eukaryotic […]

S.N. Mitochondria Chloroplasts 1. They are smaller in size (1-4 µm). They are bigger in size (4-10 µm). 2. They occur in practically all eukaryotic […]
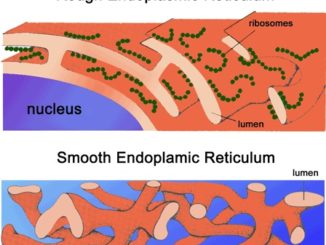
S.N. RER (Rough ER) SER (Smooth ER) 1. It is composed mainly of cisternae. It is composed mainly of tubules and vesicles. 2. It bears […]

S.N. Characteristics 70S Ribosomes 80S Ribosomes 1. Occurrence They occur in prokaryotic cells and in the mitochondria and plastids of eukaryotic cells. They occur only […]
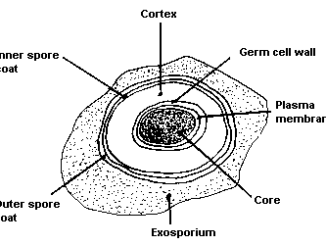
Spore is a resting or dormant cell which is metabolically inactive and is produced during unfavorable conditions like nutrition deficiency, extreme temperature and pH, presence […]
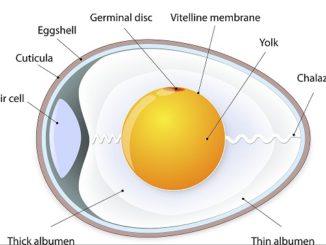
Egg cell or ovum, also known as female gamete is formed by the process of oogenesis in female organisms. They are produced by follicle cells […]
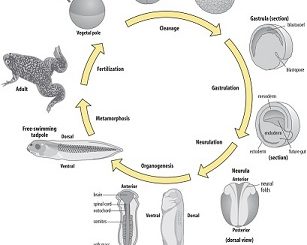
Introduction: In sexual reproduction, development of organisms begins with a fertilized egg or zygote. Zygote divides and re-divides to form an embryo. Embryo is the […]
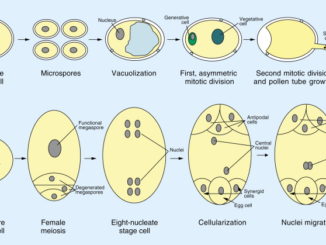
A gametophyte is the haploid phase in the life cycle of a plant that produces gametes. The process of formation of gametes or germ cells […]

S.N. Self-pollination Cross-pollination 1. Transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of the same flower (typical self-pollination) or another flower of the same […]
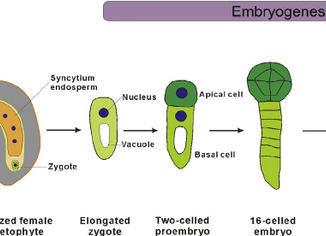
The fusion of male gamete and female gamete in sexual reproduction is called fertilization. In angiosperms, the female gamete lies deep in the ovarian cavity, […]

Generally amino acids are the end products of the digestion of dietary proteins. In humans, the degradation of ingested proteins to their constituent amino acids […]
Copyright © 2025 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes