1. Center of curvature (2F or C):
- The center of the sphere from which the lens has been cut is called the center of curvature (2F or C).
- A lens has two centers of curvature.
2. Aperture:
- The maximum portion of the spherical surface through which the refraction takes place is called the aperture of the lens.
3. Optical center (O):
- The geometrical center of the lens is known as its optical center.
- A ray of light passing through the optical center doesn’t suffer any deviation and goes straight ahead.
4. Principal axis:
- The line joining both the centers of curvature of a lens is called its principal axis.
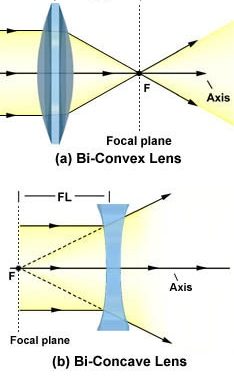
5. Principal focus or Focus (F):
- It is the point on the principal axis where the rays of light parallel to the principal axis converge after refraction through the convex lens.
- In case of concave lens, the rays of light parallel to the principal axis appear to diverge from a point on the principal axis called principal focus.
6. Focal length (f):
- The distance between the optical center and the principal focus of the lens is called its focal length.
7. Radius of curvature (R or 2f):
- The radius of the sphere from which the lens has been cut is called the radius of curvature (R or 2f).
- It is the distance between the optical center and the center of curvature in a lens.
8. Focusing:
- The process of adjusting the distance between a lens and the screen to produce a clear, sharp and distinct image in camera, microscope or telescope is called focusing.
- Rules for drawing ray diagrams:
- A diagram that traces the path, which light coming from the object takes in order for a person to view a point on the image is called a ray diagram.
- On the diagram, rays (lines with arrows) are drawn for the incident ray and the reflected or refracted ray.
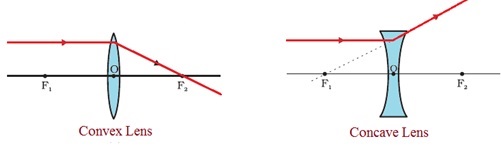
a. Rule 1:
- The ray of light which is parallel to the principal axis of a convex lens always passes through the principal focus after refraction.
- In case of concave lens, the ray appears to be diverging from the principal focus.
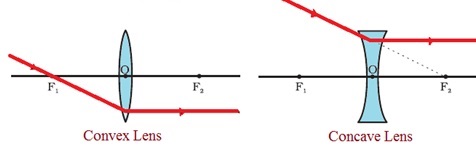
b. Rule 2:
- An incident ray passing through the principal focus of a convex lens becomes parallel to the principal axis after refraction.
- In case of concave lens, the incident ray appearing to meet the principal focus is refracted parallel to the principal axis.
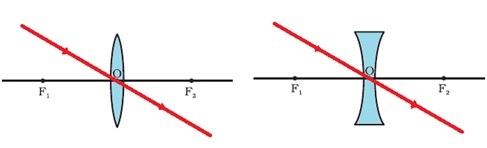
c. Rule 3:
- The ray of light that passes through the optical center of the convex lens or a concave lens goes straight without deviation after refraction.