- The lens which is thick in the middle and thin at the edges is called a convex lens whereas the lens which is thin in the middle and thick at the edges is called a concave lens.
- Convex lens is also known as a converging lens as it converges the parallel rays of light at a point after refraction.
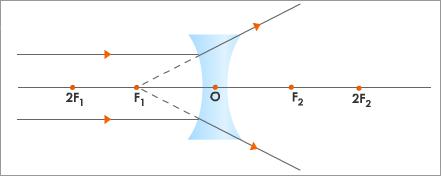
- Concave lens is also known as diverging lens as it diverges the parallel beam of light after refraction.
- The type of image formed by a convex lens depends on the position of the object that can be placed at different positions in front of the lens as follows:
- When an object is at infinity:
- The image is formed at focus (F) on the other side of the lens.
- Highly diminished
- Real and inverted
- This type of image is formed by the objective lens of an astronomical telescope and a camera lens focused at infinity.
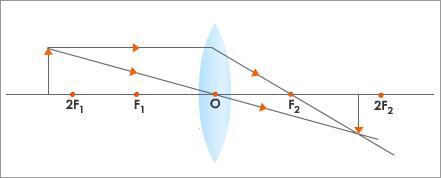
- When an object is beyond 2F:
- The image is formed between F and 2F on the other side of the lens.
- Diminished
- Real and inverted
- This type of image is formed in a photographic camera.
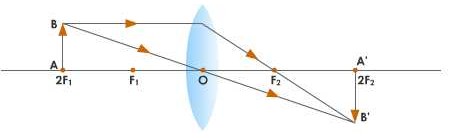
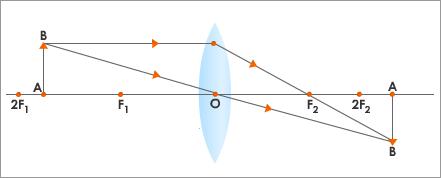
- When an object is at 2F:
- The image is formed at 2F on the other side of the lens.
- Same size as the object
- Real and inverted
- This type of image is formed by a terrestrial telescope.
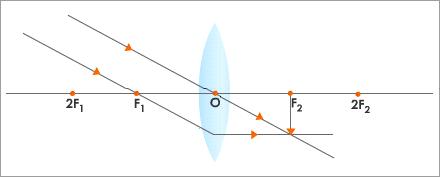
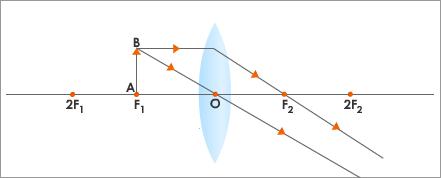
- When an object is between 2F and F:
- The image is formed beyond 2F on the other side of the lens.
- Enlarged or magnified
- Real and inverted
- This type of image is formed in film and slide projectors to produce an enlarged image on the screen.
- When an object is at F:
- The image is formed at infinity on the other side of the lens.
- Highly enlarged or magnified
- Real and inverted
- This type of image is formed by search lights and spot lights in theaters.
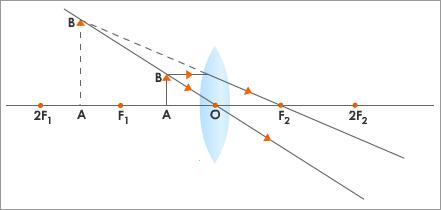
- When an object is between F and O:
- The image is formed beyond the object on the same side of the lens.
- Enlarged or magnified
- Virtual and erect
- This type of image is formed by a simple microscope and a hand lens.
The image formed by concave lens is always diminished, erect and virtual.
- When an object is at infinity:
- The image is formed at focus on the same side of the lens.
- Point sized (highly diminished)
- Virtual and erect
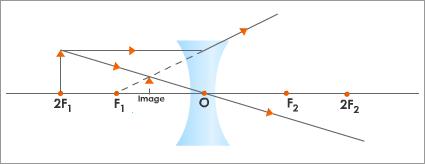
- When an object is kept anywhere between infinity and the optical center:
- The image is formed between F and O on the same side of the lens.
- Diminished
- Virtual and erect
- This type of image is formed by spectacles for correcting myopia or short sightedness.
9. When the Object is Placed between O and F:
- The image is formed between O and F on the same side of the lens.
- Diminished
- Virtual and erect
Images source: https://physics.tutorvista.com/light