- E. Starling coined the term “hormone” in connection with the discovery of Secretin.
- Hormones are organic compounds secreted in small quantities that regulate the plant’s activities after being translocated to the organ or site of reaction where they show their specific effect.
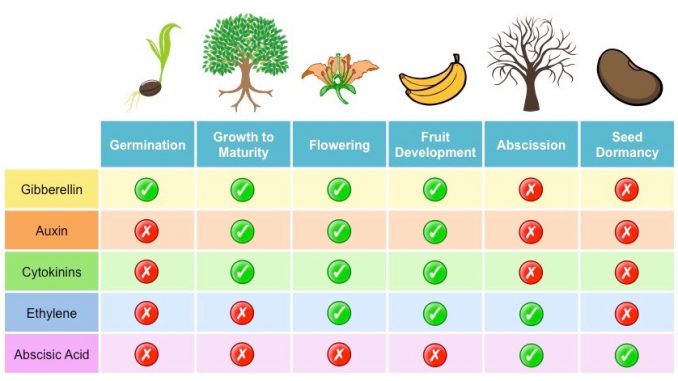
- Five major kinds of plant hormones are as follows:
- Auxins
- Cytokinins
- Gibberellins
- Ethylene
- Abscisic acid
- Auxins:
- Existence of growth substance in plants was proposed by Charles Darwin in his book “The power of movements in plants” while working on Canary grass (Phalaris cannariensis).
- W. Went discovered auxins by Avena curvature test.
- In 1931, Kogl and Haagen Smit isolated an active substance from human urine and named as Auxin-A (Auxintriolic acid).
- In 1934, they isolated similar active substance from corn grain oil and was named as Auxin-B (Auxinolonic acid). Neither of these two Auxins has ever been isolated again.
- Re-examination of human urine by Kogl et.al and examination of Rhizopus culture by Thimann (1935) led to the isolation of different substances, which was named as heteroauxins.
- Heteroauxins are identical with indole-3-acetic acid.
- Indole-3-acetic acid is considered as true natural auxin, which is found in most plants including Avena
- Synthetic auxins are: Nephthalene acid (NAA), indole butyric acid (IBA), indole propionic acid (IPA), 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), 2,4,5-Trichlorobenzoic acid (2,4,5-T)etc.
- Synthesis of auxin takes place from the amino acid tryptophan.
- Auxin shows polar transport.
Funtions of Auxins:
- Elongation of the cell.
- Apical dominance: suppresses the growth of lateral buds.
- Root initiation: high concentration of auxins inhibits the elongation of roots but increases the number of lateral roots.
- IAA induces rooting.
- NAA, IBA, IPA induce rooting of cuttings.
- 2,4-D and 2,4,5-T both are weed killers.
- Methyl ester of Nephthalene acetic acids is used for preventing sprouting of potato.
- Foliar spray of NAA and 2,4-D causes flowering of litchi and pineapple.
- Auxin controls abscission (the natural detachment of parts of plant, normally dead leaves and ripe fruits) of fruits.
- Auxins also stimulate cell wall synthesis and parthenocarpy.
- Cytokinins (kinetins):
- They are also called kinetins.
- Cytokinin was extracted from old stock of degraded DNA by Miller and Skoog.
- Chemically, cytokinin is 6-furfuryl amino-purine.
- Overbeek et.al gave the name cytokinin because it stimulates cytokinesis (cell division).
- It has been isolated from plant extracts like milk of coconut and old DNA extract.
- Zeatin belonging to kinin group of hormones was extracted from maize kernel.
- They are produced in actively growing tissues such as embryos, developing fruits and roots.
Functions of Cytokinins:
- Activates cell division.
- Formation of callus occurs if ratio of Auxin and Cytokinin is equal.
- More Auxin and less Cytokinin results in root initiation whereas more Cytokinin and less Auxin results in bud formation.
- Induces initiation of interfascicular cambium.
- Stimulates cell elongation resulting in the expansion of cotyledons and foliage leaves (shoot development).
- Counteraction of apical dominance (induces growth of lateral buds).
- Prevents ageing and senescence in plants.
- Gibberellins:
- They were first isolated from a fungus Gibberella fugikuroi/ Fusarium moniliforme which caused a disease known as foolish seedling or bakanae disease in rice plant.
- Up to date, more than 100 naturally occurring gibberellins have been identified.
- Widely studied Gibberellin is Gibberellic acid (GA3).
Functions of Gibberellins:
- Seed germination: induces seed germination in light sensitive seeds even in dark after its treatment with the hormone. E.g. lettuce and tobacco.
- Gibberellins stimulate stem elongation and leaf expansion.
- Genetically dwarf plant grows tall after gibberellins treatment. E.g. corn, pea.
- Causes parthenocarpy in pome fruits.
- Helps to break dormancy in potato tubers and tree buds in winter.
- Induces flowering in long day plants in short days.
- In monoecious plants, spraying of gibberelins increases the number of male flowers.
- De novo (a new) synthesis of α-amylase in the alurone layer of epidermis of cereal grains during germination.
- Ethylene:
- It is the only gaseous hormone.
- It consists of an amino acid, methionine.
- O2 is a promoter and CO2 is an inhibitor for its synthesis.
- It is mostly released from roots, shoot meristems and ripening fruits.
Functions of Ethtylene:
- It induces ripening of fruits. Mature fruits also release ethylene.
- It accelerates abscission of leaves, stems, flowers and fruits.
- It induces flowering in pineapple.
- Treatment of plants with ethylene increases the number of female flowers and fruits in cucumbers.
- Induces epinasty (the outward and often downward bending of plant parts) in leaves.
- Abscisic acid (ABA):
- A substance strongly antagonistic to growth was isolated by Addicott from young cotton fruits and named it Abscisin II.
- Wareing et. Al pointed the presence of an active substance in birch leaves which inhibited growth and induced dormancy of buds. It was named as Dormin.
- Later on, both Abscisin II and Dormin were found to be same and named as Abscisic acid.
- It is mainly produced in mature leaves, stem, fruits and seeds.
Functions of Abscisic acid:
- It accelerates abscission.
- Maintains dormancy of seeds.
- It also accelerates senescence in leaves.
- It causes the closing of stomata.