- The endocrine system is made up of tissues or organs (collectively called glands) which secrete a chemical substance called hormone.
- Hormone is a specialized chemical substance secreted by endocrine glands (ductless glands) and released into the blood stream.
- They travel to all parts of the body through blood but are effective in extremely small amount to produce a dramatic response in the target cells which are located far away from the glands.
- The study of endocrine glands, the hormones they secrete and their mode of action is called endocrinology.
- The endocrine system:
- Regulates the concentration of chemicals in body fluids and the metabolism of proteins, lipids and amino acids.
- Co-ordinates with the nervous system to help the body react to stress and stimuli properly.
- Regulates growth and development, including sexual development and reproduction.
Pituitary gland:
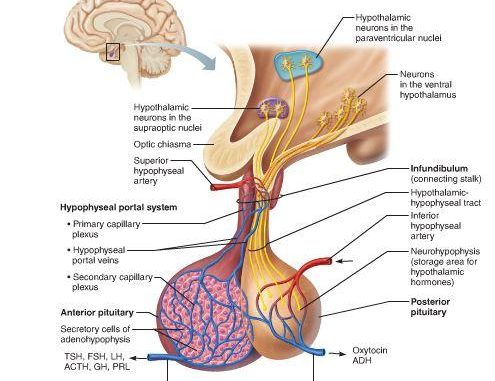
- It is located directly just below the hypothalamus of brain and is held by an infundibular stalk.
- It is about 1 cm long, 1 to 1.5 cm wide and 0.5 cm thick (about the size and shape of a pea).
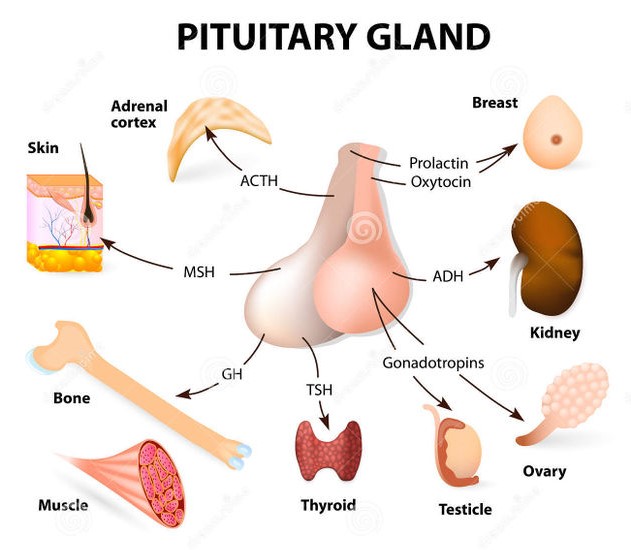
- It is also known as the master gland because the hormones released by this gland regulates and controls the secretions of other endocrine glands in our body.
- Pituitary gland itself is under the control of hypothalamus, hence also called the hypophyseal gland.
- The pituitary gland has two distinct lobes:
- The anterior lobe (Adenohypophysis)
- The posterior lobe (Neurohypophysis)
- Between these two lobes is a small zone called the pars intermedia.
- The anterior lobe is larger with more than 75% of the total weight of the gland and abundance of functional secretory cells.
- The posterior lobe has a greater supply of large nerve endings.
Hormones of the Neurohypophysis:
- It doesn’t secrete hormone but stores hormones secreted by the hypothalamus which is brought to it by nerve fibers (hypothalamus-hypophyseal tract).
- It has spindle shaped cells called pituicytes. The hormones are:
1. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH):
- It is a polypeptide and is also known as vasopressin.
- It causes the contraction of arterial walls increasing blood pressure.
- It also promotes the reabsorption of water from the distal convoluted tubules of nephrons in kidneys.
- Its deficiency (hyposecretion) causes diabetes insipidus, i.e. micturition increases (frequent urination).
2. Oxytocin:
- It is a polypeotide.
- It stimulates parturition (the contraction of pregnant uterus), so called a birth hormone.
- It also induces lactation (milk ejection from breasts after childbirth), so called milk ejection hormone.
Hormones of the Adenohypophysis:
- It synthesizes 5 tropic or stimulating hormones (whose primary target is another endocrine gland).
- The 2 non tropic hormones are growth hormone and prolactin, which are involved with growth and milk production respectively.
1. Growth hormone (Somatotropin):
- It is a polypeptide (protein).
- It stimulates the growth rate of body by increasing the tissue mass (protein synthesis), maintaining epiphyseal growth of bones and stimulating cell division.
- Hyposecretion in young person causes dwarfism (marked closure of epiphyseal disks of bones and no growth of body).
- Hypersecretion in young person causes gigantism (the person continues to grow to 7 to 8 feet, looking like a giant).
- After normal growth has stopped, overproduction of growth hormone causes acromegaly (bones in head, hands, and feet start thickening rather than lengthening).
2. Prolactin:
- It is a polypeptide.
- It promotes breast development during pregnancy.
- It stimulates milk production from the mammary glands of mother after childbirth.
*milk ejection (not milk production) is stimulated by oxytocin.
3. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH):
- It is glycoprotein in nature and stimulates the production and secretion of thyroid hormones (Thyroxine).
4. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH):
- It is also called corticotropin.
- It stimulates the secretion of adrenal cortex steroids (glucocorticoids).
5. Luteinizing hormone (LH):
- It is glycoprotein in nature and is also called a gonadotropin.
- In females, it stimulates the development of corpus luteum, release of oocyte (ovum) and the production of progesterone and estrogen.
- In males, it stimulates the secretion of testosterone and the development of interstitial tissue of testes.
6. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH):
- It is glycoprotein in nature.
- In females, it stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles and ovulation.
- In males, it stimulates the production of sperm.
7. Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH):
- It is also known as intermidin.
- It is apparently involved with the distribution of melanin (skin pigment produced by melanocytes) in combination with the ACTH.