
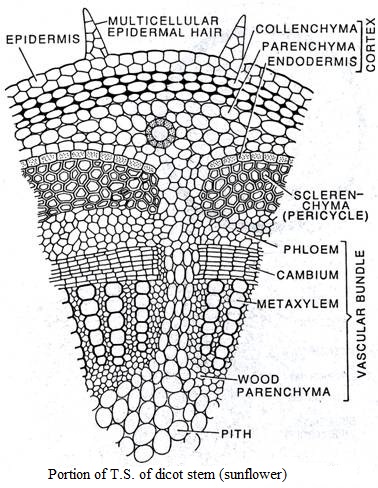
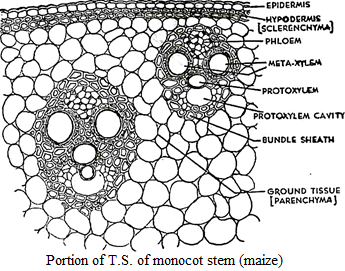
| S.N. | Dicotyledonous stem | Monocotyledonous stem |
| 1. | Internally, the stem is differentiated into epidermis, hypodermis, cortex, endodermis, pericycle, stelar system and pith. | Internally, the stem is differentiated into epidermis, hypodermis and ground tissue. i.e. cortex, endodermis, pericycle and pith are absent. |
| 2. | Hypodermis is usually collenchymatous. | Hypodermis is usually sclerenchymatous. |
| 3. | Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring. | Vascular bundles are scattered in the parenchymatous ground tissue. |
| 4. | Parenchymatous medullary rays occur in between the vascular bundles. | Medullary rays are absent. |
| 5. | Bundle sheath is absent. | Vascular bundles are surrounded by sclerenchymatous bundle sheath. |
| 6. | Vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral or bicollateral, endarch and open. | Vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral or concentric, endarch and closed. |
| 7. | Vascular bundles are limited in number. | Vascular bundles are numerous. |
| 8. | Xylem vessels are generally polygonal in transaverse section. | Xylem vessels are generally oval in transverse section. |
| 9. | Lysigenous cavity in xylem is absent. | Lysigenous cavity is present in xylem. |
| 10. | Phloem is composed of sieve tubes, companion cells and phloem parenchyma. | Phloem is composed of sieve tubes and companion cells only. i.e. phloem parenchyma is absent. |
 |
 |