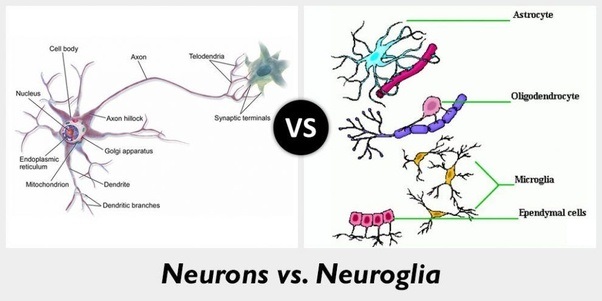
| S.N. | Nerve cells | Glial cells |
| 1. | They are neuronal cells and are also called neurons. | They are non-neuronal cells and are also called neuroglia. |
| 2. | They have relatively small cell body and long processes. | They have a relatively large cell body and short processes. |
| 3. | The processes arise from the two opposite ends of the cell body. | The processes arise from nearly all over the cell body. |
| 4. | There are two types of processes; short dendrites and a long axon. | The processes are all alike with no differences. |
| 5. | Neurons occur end-to-end in chains. | Glial cells are aggregated in masses. |
| 6. | They produce and conduct nerve impulses. | They don’t conduct nerve impulse but maintain homeostasis, form myelin sheath and provide support and protection for neurons. Some glial cells (microglia cells) are phagocytic. |
| 7. | All neurons arise from the ectoderm. | Most glial cells arise from the ectoderm; microglia cells arise from the monocytes. |
| 8. | They form synapses between neurons for the conduction of nerve impulse. | They don’t form synapses. |