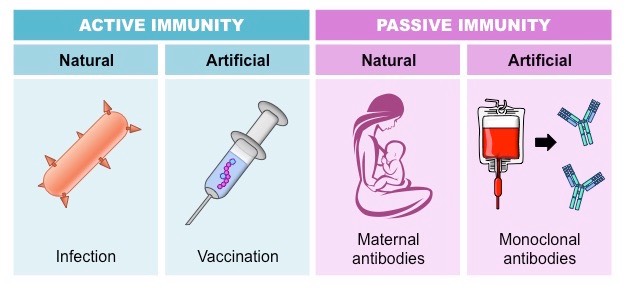
| S.N. | Active immunity | Passive immunity |
| 1. | Host itself produces antibodies to provide immunity. | The antibodies produced in other hosts in passively received by the host. |
| 2. | The immune system of the host actively participates. | The host’s immune system doesn’t participate. |
| 3. | It is induced by natural infection or vaccination (after contact with immunogen). | It is conferred by the injection or introduction of preformed or readymade antibody in the host. |
| 4. | Immune response is durable and more effective. | Immune response is short lived and less effective. |
| 5. | Immunity develops only after the lag period. | Lag period is absent and hence immunity becomes effective immediately. |
| 6. | It is used for prophylaxis to develop or induce resistance against microorganisms (antigens). | It is applied for the treatment of certain disease like rabies and acute infections. |
| 7. | It is not applicable for immune-deficient hosts. | It is useful in immune-deficient host that cannot produce antibody by itself. |
| 8. | Immunological memory is present due to presence of memory cells. | There is no immunological memory. |
| 9. | Subsequent challenge with the booster dose is more effective in immunity development. | Subsequent administration of antibody is less effective due to ‘immune elimination’. |
| 10. | After antigenic stimulus, negative phase may occur due to antigen combining with any pre-existing antibody in blood. | There is no negative phase. |