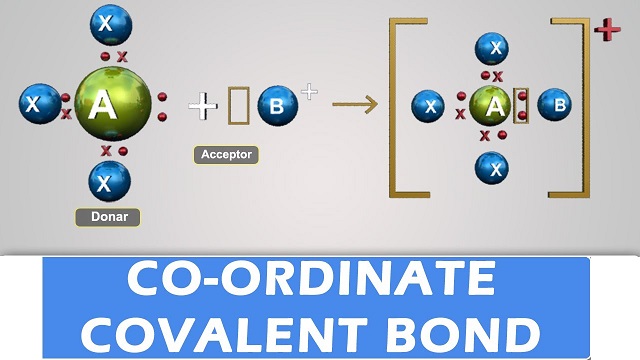
- Co-ordinate covalent bond is a special type of covalent bond.
- When both the electrons of the electron pair, to be shared equally between two atoms, are contributed by a single atom, the bond formed is said to be co-ordinate covalent bond and the compound thus formed is called a co-ordinate covalent compound.
- The co-ordinate covalent bond is said to have co-ordinate valency.
- Among the two atoms in a co-ordinate covalent bond, one has a complete octet and at the same time possesses at least a pair of unused electrons while the other is short of two electrons.
- The atom which contributes the pair of electrons is called a donor and the one which accepts the pair of electrons is known as a receptor.
- The unused pair of electrons in a donor is known as lone pair of electrons.
- Co-ordinate covalent bond is signified by an arrow pointing from the donor atom towards the receptor.
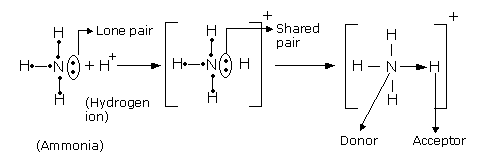
- In the formation of co-ordinate linkage (or bond), a partial positive charge is developed on donor and a partial negative charge is developed on the receptor atom.
- The co-ordinate covalent bond once formed is indistinguishable from a covalent bond, the only difference being simply in the way of formation of the bond.
General properties of co-ordinate covalent compounds:
- Physical state: They are generally liquids and gases.
- Melting and boiling points: The melting and boiling points of such compounds is comparatively higher than that of covalent compounds and lower than that of electrovalent or ionic compounds.
- Electrical conductivity: Since they have semi-ionic nature, they are poor conductors of electricity.
- Solubility: They are sparingly soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents because they have semi-polar behavior.
- Directional character: The co-ordinate covalent bond is also rigid and directional and therefore, the structure of such compounds holds out possibilities for space isomerism just as in pure covalent compounds.