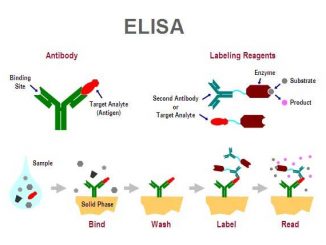
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Principle, types and applications)
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, commonly known as ELISA or EIA is one of the most sensitive techniques for detecting antigen or antibody. The reaction between an […]

Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, commonly known as ELISA or EIA is one of the most sensitive techniques for detecting antigen or antibody. The reaction between an […]
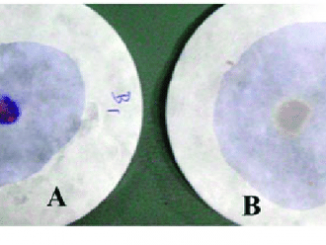
Principle: This test is performed to determine or identify the presence of an enzyme cytochrome oxidase (of the electron transport chain) in bacterial cells. The […]

Principle The enzyme catalase, which is produced by many aerobic and facultative anaerobic microorganisms, neutralizes toxic forms of oxygen metabolites like hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and […]

Kingdom Mycota consists of eukaryotic organisms. Fungi exist in two fundamental forms; multicellular, filamentous or hyphal form (molds) and unicellular or budding form (yeast). They […]
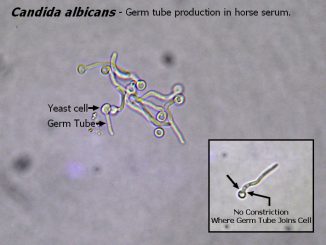
Germ tube is a young hypha (short, non-nucleated and non-septate) growing out of a yeast cell or spore (in spore-releasing fungi) during their germination. They […]

General properties: Man appears to be the sole reservoir of H.pylori and it colonizes the gastric mucosa of almost one in four of the adult […]
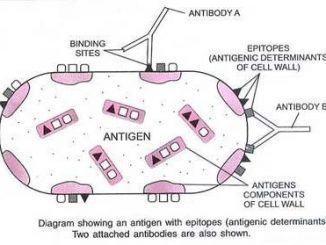
A protein or carbohydrate that evokes our immune system and initiates the immune response is called an immunogen. Immunogens are associated with an infectious agent […]
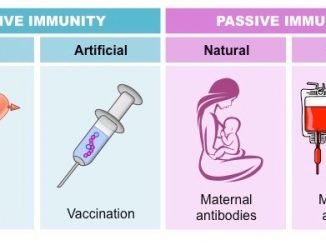
S.N. Active immunity Passive immunity 1. Host itself produces antibodies to provide immunity. The antibodies produced in other hosts in passively received by the host. […]
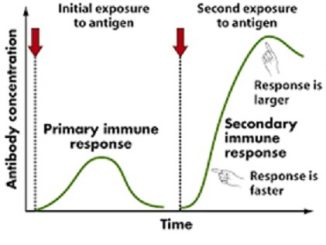
When an antigen is introduced for the first time in a host, it activates T and B cells. Activation of B- cells produces memory cells […]
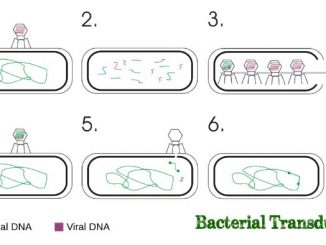
Transduction is the transfer of gene or portion of DNA from one bacterium (donor) to another (recipient) mediated by a bacteriophage. In transduction, the bacteriophage […]
Copyright © 2025 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes