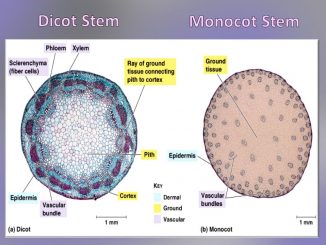
Differences between Dicot and Monocot stem
S.N. Dicotyledonous stem Monocotyledonous stem 1. Internally, the stem is differentiated into epidermis, hypodermis, cortex, endodermis, pericycle, stelar system and pith. Internally, the stem is […]

S.N. Dicotyledonous stem Monocotyledonous stem 1. Internally, the stem is differentiated into epidermis, hypodermis, cortex, endodermis, pericycle, stelar system and pith. Internally, the stem is […]

General features of flowering plants Previously, all the flowering plants were kept in the sub-kingdom called Phanerogams. They are the most developed and economically important […]

General characteristics of plants: This kingdom includes autotrophic (some are heterotrophic), eukaryotic and multicellular organisms (some are however, unicellular like Cholerlla, Chlamydomonas) They live in […]
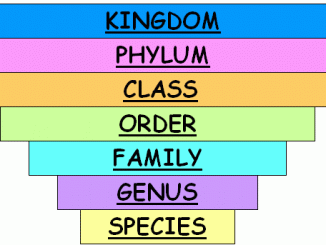
The scientific ordering or systematic arrangement of living organisms in a hierarchical series of groups on the basis of their relationships (morphological, evolutionary and other […]

Based on the results obtained from the experiments on pea plant with contrasting characteristics for 8 continuous years, Gregor Johann Mendel formulated the three basic […]

The structural features of living organisms that develop over a period of time to enable them to survive and reproduce in a particular environment is […]

Vegetative propagation is a form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment of the parent plant or grows from a specialized […]
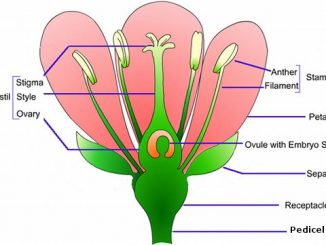
Flowers are the reproductive organs in Angiosperms. A flower is borne on a stalk called pedicel with an upper swollen region known as thalamus. A […]
Copyright © 2025 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes