
- Tollen’s test is a chemical test used to distinguish reducing sugars from non-reducing sugars.
- It is also known as silver mirror test since free silver metal is formed at the end of this test reaction.
- It also helps in the differentiation of aldehydes and ketones through routine qualitative organic analysis.
Principle:
- Reducing sugars or aldehydes react with Tollen’s reagent (ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate) to reduce it to form free silver metal.
- Tollen’s reagent is an alkaline solution of silver nitrate (AgNO3) mixed with liquid ammonia (NH3) which results in the formation of a complex.
- Brown ppt of silver oxide (Ag2O) is formed when AgNO3 reacts with NaOH.
- Silver oxide is then dissolved by aqueous ammonia to form a complex, [Ag(NH3)2]NO3.
- This complex in Tollen’s reagent is a strong oxidizing agent that oxidizes the aldehyde group present in some carbohydrates to form a carboxylic acid.
- The silver ions present in the reagent are reduced to free metallic silver which forms a silver mirror on the bottom and sides of the test tube.
- Ketones generally give negative Tollen’s test. However, an α-hydroxy ketone gives a positive test since it is oxidized into an aldehyde by Tollen’s reagent.
Principle reactions:
2AgNO3 + 2NaOH → Ag2O (brown ppt) + 2NaNO3 + H2O
Ag2O (brown ppt) + 4NH3 + 2NaNO3 + H2O → 2[Ag(NH3)2]NO3 + 2NaOH
Glucose + 2[Ag(NH3)2]NO3 + H2O → 2 Ag(silver mirror) + 4 NH3 + Gluconic acid + 2H+
Requirements:
- Sample solution
- Tollen’s reagent (Ammoniacal solution of silver nitrates)
- Test tubes
- Pipette
- Water bath
Procedure:
- First of all, two clean and dry test tubes are taken and labeled as test (T) and blank (B).
- 1 ml each of sample solution and distilled water are pipetted into tubes T and B respectively.
- 2 ml of Tollen’s reagent is added to both the test tubes.
- The test tubes are kept in warm water bath for 3-5 minutes.
- The color formation is observed and noted down.
Result interpretation:
https://pixels.com/featured/2-silver-mirror-test-andrew-lambert-photography.html
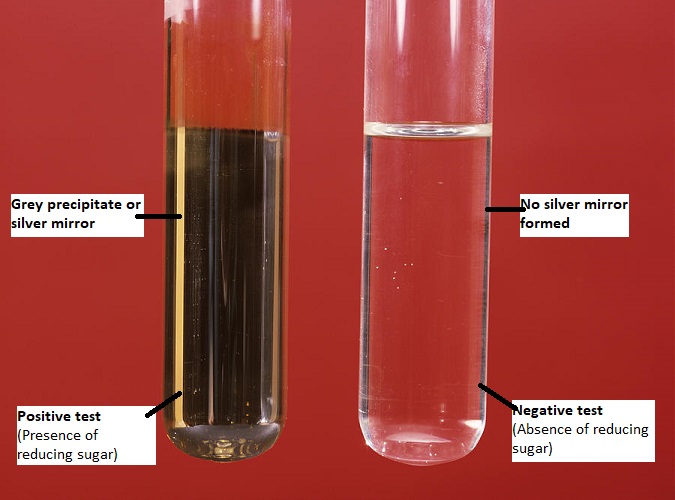
- If a dark grey precipitate or silver mirror is formed on the bottom and sides of the test tube, it indicates a positive result. It confirms the presence of reducing sugars/ aldoses/ α-hydroxy ketoses in the sample solution.
- The absence of such precipitate means a negative result. i.e. absence of reducing sugars/ aldoses/ α-hydroxy ketoses in the sample solution.
Limitations:
- Tollen’s reagent must be prepared immediately prior to its use as an explosive substrate can be formed if it is allowed to dry.
- The glassware must be rigorously cleaned with concentrated KOH (Potassium Hydroxide) because if they are not perfectly clean, a dark precipitate instead of grey may appear in the solution.
- Some carbohydrates devoid of aldehyde group might give a positive result because of the isomerization of such sugars under alkaline conditions.
Tollen’s test or Silver mirror test: Principle, Requirements, Procedure, Result Interpretation and Limitations