- Carbon is a basic component of plants and animals.
- There is a continuous exchange of carbon dioxide between the atmosphere, aquatic bodies and living organisms.
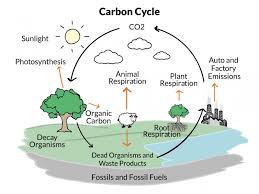
- Thus, carbon cycle can be defined as the cyclic process in which carbon element is circulated continuously through the living and non-living components of the biosphere.
- Carbon is the most essential constituent of all the organic compounds and a major element involved in the fixation of energy by photosynthesis.
- Carbon dioxide gas occupies about 0.03% of the atmosphere by volume which is an important source of carbon.
- It is found in petroleum products and rocks like limestone, shells of organisms in the form of carbonates.
- It is also found in living organisms in the form of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, nucleic acids and other complex compounds.
- During photosynthesis, all green plants utilize carbon dioxide gas to prepare starch, i.e. food.
- When animals eat plants, plant carbohydrate is converted into animal carbohydrate.
- Both plants and animals throw out carbon dioxide in the process of respiration which is returned to the atmosphere.
- When plants and animals die, decomposers like bacteria and fungi act on their dead bodies and produce carbon dioxide which gets mixed in the atmosphere.
- Some of the plants and animals get buried deep under the earth crust for many years whose bodies change into fossil fuels like petroleum, coal etc. through chemical changes.
- Fossil fuels like petrol, diesel, kerosene, coal etc. are used as a source of heat energy for domestic purpose, in automobiles and in industries.
- When these fossil fuels burn, they give off carbon dioxide gas which is mixed in the atmosphere.
- Some carbon dioxide dissolved in water gets converted into calcium carbonate in limestone and other carbonate rocks.
- When acid rain comes in contact with such rocks, carbon dioxide gas is released.
- Volcanic eruptions and hot springs also release carbon dioxide.
- In this way, plants and animals use carbon and its compounds from nature and then return them to the nature in one way or the other. This is how carbon cycle is maintained in nature.