- Mature sperm or spermatozoan is a male gamete that takes part in reproduction.
- Normally, 300 to 500 million sperm are released during an ejaculation.
- A male releasing less than about 20 to 30 million sperm tends to be infertile.
- Sterile males don’t produce viable sperm.
- Sterility may be the result of sexual transmitted diseases (STDs) or of diseases like mumps, which destroy the lining of the seminiferous tubules.
Formation of sperm:
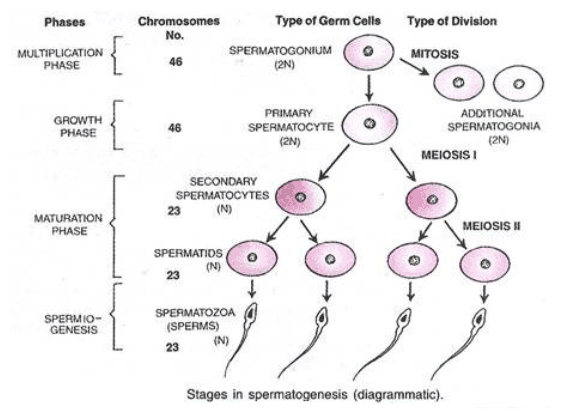
- The process of formation of spermatozoa or sperm in seminiferous tubules in testes is called spermatogenesis.
- They are constantly being produced in the seminiferous tubules in testes, which always contain sperm in various stages of development.
- With the onset of puberty, when a boy us 11-14 years old, dormant, unspecialized germ cells called spermatogonia are activated by the secretions of testosterone.
- Each spermatogonium divides through mitosis to produce two daughter cells, each containing the full set of 46 chromosomes.
- One of the two daughter cells is the spermatogonium which continues to produce daughter cells. The other daughter cell is called a primary spermatocyte, a large cell that moves toward the lumen of the seminiferous tubule.
- The primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis to produce two smaller secondary spermatocytes, each with 23 chromosomes: 22 autosomes and 1 X or Y sex chromosome.
- Both secondary spermatocytes undergo the second meiotic division to form four final primitive germinal cells, the spermatids, which still have only 23 chromosomes.
- The spermatids develop into mature sperms without undergoing any further cell division.
- Each sperm requires about 64 days (2 months) for its complete development.
- The final maturation of a sperm takes place in the epididymis lying on the surface of each testis.
Structure of a sperm:

- A sperm is one of the smallest cells in the body.
- Its length from tip of the head to the tip of the tail is about 0.05mm.
- Each sperm consists of three parts; a head, a middle piece and a tail.
- The tip of the head possesses an acrosome containing several enzymes that help the sperm fuse with the egg cell membrane and penetrate it during fertilization.
- In the center of the head is a compact nucleus containing chromosomes (with all the genetic material and information).
- Since spermatogenesis occurs by meiotic cell division, the number of chromosomes in sperm is haploid (n).
- The middle piece consists mainly of coiled mitochondria, which supply ATP (energy) for the motility of the sperm.
- The beating movement of the undulating tail (flagellum) drives the swimming sperm forward.
- The ability to swim, called motility, is essential for male fertility.
Process of sperm formation and its structure