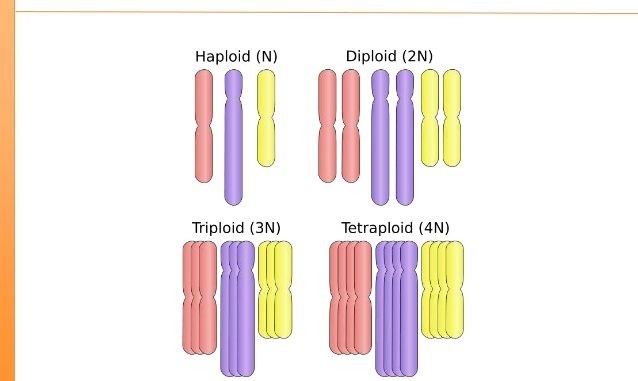
- Mutation caused by the change in the number of chromosomes in an organism is called ploidy or genomatic mutation.
- It is further of two types:
- Aneuploidy
- Euploidy
- The phenomenon in which the organism has more than two sets of chromosomes in its cell is called polyploidy and such organisms are called polyploids.
- Polyploids can either be:
- Triploid : organisms with 3 sets of chromosomes (2n+n)
- Tetraploid: organisms with 4 sets of chromosomes (2n+2n)
- Pentaploid: organisms with 5 sets of chromosomes (2n+2n+n)
- Hexaploid: organisms with 6 sets of chromosomes (2n+2n+2n)
- Polyploidy is more common in plants than animals. About one third of all plants are polyploids which may arise either naturally or artificially.
Causes of polyploidy:
- Normally, the chromosomes under replication separate during cell division.
- But if the cytoplasm fails to cleave, a tetraploid is formed. A doubling of the number of somatic chromosomes in a sex organ results into doubling of the number of gametic chromosomes.
- A fusion of a diploid and a haploid gametes results into triploid organism, while the fusion of two diploid gametes produces a tetraploid individual.
- Even abnormal meiosis may result into diploid gamete instead of a haloid gamete formation.
- Polyploidy may also occur if an ovum or egg is fertilized by more than one male gamete.
Types of polyploidy:
- Depending on whether polyploids are produced by the multiplication of chromosome sets that are initially from a single species or from two different species, polyploidy is classified into two types:
- Autopolyploidy
- Allopolyploidy
- Autopolyploidy:
- Autopolploids are those polyploids , which are derived from the multiplication of the same basic set of chromosomes.
- In this case, multiple genomes are identical, being produced by the duplication of the same genomes.
- Thus, homologous chromosomes come from the same species. For example, if a diploid species has two similar sets of chromosomes or genomes (AA), an autotriploid wil have three similar genomes (AAA) and an autotetraploid will have four such genomes (AAAA).
- Autopolyploids are vigorous and large sized. Tomato, strawberry, grapes are autopolyploid races.
- Autotriploids are usually sterile and cannot produce seeds, therefore, it is used in produced seedless varieties of economic plants like watermelons, grapes, banana etc.
Artificial induction of autopolyploidy:
- Autopolyploidy can be induced artificially by the application of :
- Chemicals like colchicine
- Radioactive substances like Radium and X-rays
- Alternate heat and cold shocks
- The chemicals are usually applied to actively dividing meristematic cells. The chemical acts on spindle apparatus, whose formation is arrested and so mitosis or meiosis becomes abnormal.
- The absence of spindle fibers cause non-segregation of already duplicated chromosomes and as a result, a single tetraploid nucleus is formed, if the parent is diploid.
- Allopolyploidy:
- Allopolyploids are those polyploids which are formed due to the doubling of chromosomes number in a hybrid.
- The homologous sets are non-homologous and are initially derived from two different species.
- Such polyploid species often have greater tolerance for adverse climatic conditions and have a greater economic value.
- A hexaploid species of wheat was artificially synthesized in 1946.
- A species of wheat Triticum monococcum (2n=14) was bred with wild grass Aegilops speltoides (2n=14) to produce a different species of wheat called Emmer wheat, Triticum durum (2n=28), a tetraploid condition.
- Emmer wheat was again crossed with another species of wild grass Aegilops squarrosa (2n=14) to produce the wheat Triticum aestivum (2n=42), a hexaploid (6n) condition.
Polyploidy in animals:
- Polyploidy is rare in animals.
- It occurs in flatworms, leeches and mice.
- In the liver of mouse, about 40% of the cells are tetraploid and about 5% are octaploids.
- Polyploidy in humans have been found in liver cells and cancer cells.
- Diploid human cells have 46 chromosomes each, but in cancer cells, this number may reach 100 or more due to abnormal divisions.
- In such condition, polyploidy, whether complete or mosaic, leads to gross abnormalities and death.
Role or significance of polyploidy:
- Polyploidy is one of the sources of variation and thus helps in evolution of new varieties, species and genera.
- Polyploidy is often associated with advantageous features such as increased size, hardness. This is called hybrid vigour.
- Seedless varieties of watermelons, tomatoes, grapes etc. have been produced by triploids.
- Disease resistant and high yielding species of crop plants such as hybrid wheat, hybrid paddy are produced by allopolyploidy.
- Polyploidy is usually used in obtaining fodder plants; as the leaves, flowers, fruits of polyploids are usually larger in comparison to a diploid variety.
- Polyploid plants have more morphological, genetic and physiological advancements over a normal diploid plant and a polyploid plant often faces the ecological hazards more boldly.