- Ovary is the most important part of the carpel as it contains ovules that develop into seeds after fertilization.
- The ovary may consist of different chambers inside of it, called locules.
- The ovules develop from a special tissue called placenta in the locules.
- The arrangement or distribution of placentae in the cavity of the ovary is known as placentation.
- The most common types of placentation found in plants are as follows:
- Marginal placentation:
- The placenta forms ridges along the ventral suture of the ovary.
- The ovules are borne on this ridge forming two rows.
- This is found in leguminous plants. Example: gram, peas, beans.
- Parietal placentation:
- The placenta is situated on the meeting of two margins of subsequent carpels which may be two or more in number.
- In this type of placentation, the ovules develop on the inner wall of the ovary.
- Ovary has a single chamber but appears to be double-chambered because of the formation of a false septum called replum.
- This is found in plants of the family Crucifereae. Example: Mustard and Argemone.
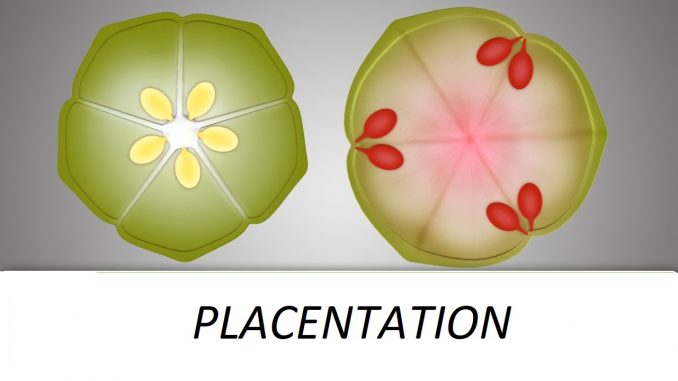
- Axile placentation:
- Ovules are borne at or around the center of a multi-chambered ovary (multilocular) on an axis formed from joined septa.
- Axile placentation is found in plants of the family Solanaceae. Example: lady’s finger, tomato.
- Basal placentation:
- The placenta is situated at the base (bottom) of the ovary and a single ovule is borne on it.
- This is found in plants of the family Compositae. Example: sunflower, marigold.
- Free central placentation:
- Placenta arises from the base of the ovary and the ovary is unilocular (no septum).
- Ovules arise from the central axis.
- It is found in plants like Primula (Primose).
- Central placentation:
- The ovules develop from the central axis of the multi-locular ovary.
- The ovary looks unilocular due to the breaking of partition walls.
- Example: Dianthus (family Caryophyllaceae).
- Superficial placentation:
- Ovules arise from the inner wall of the septa in a multilocular ovary.
- Example: water lily (family Nympheaceae).
