General features:
- They are commonly called soft bodied animals.
- They are mostly marine, few fresh water and also found in damp soil.
- It is the second largest phylum in the animal kingdom.
- Body is unsegmented (except Neoplina) and bilaterally symmetrical (except few twisting forms like Pila).
- They have organ system grade of body organization.
- Body is triploblastic and haemocoelomte.
- Body is divided into three distinct parts; foot for locomotion, head bears sense organs and visceral mass (digestive and circulatory organs).
- Body is covered by calcareous shell that may be external (e.g. Pila), internal (e.g. slug, sea hare, sepia) and absent (e.g. sea lemon, octopus).
- Glandular fold of the body is called mantle or pallium.
- Mantle cavity or pallial cavity is located between shell and visceral mass.
- Body wall:
- It consists of single layered epidermis which is ciliated.
- Muscles are unstriped and occur in a bundle.
- Digestive tract:
- Alimentary canal is complete and the mouth is guarded by operculum attached to foot.
- In some animals like Pila gut is provided with rasping organ called radula and odontophore with rows of 7 teeth.
- Respiratory organs:
- Aquatic forms respire through comb like gills called ctenidia whereas terrestrial forms respire through pulmonary sac.
- Sense organs:
- Oshphradium (olfactory organ) are present which that test the chemical nature of ingoing water current.
- Eyes act as photoreceptors, located on the tip of the tentacles.
- Statocysts are the balancing organs. Tentacles are tactile organs.
- Circulatory system:
- It is generally of open type except cephalopods.
- The heart is myogenic and dorsally
- Blood is blue in color due to the presence of copper containing respiratory pigment called Hemocyanin.
- Excretory system:
- They are ammonotelic.
- One or two pairs of sac like kidneys or organs of Bojanus are present.
- Gills are also excretory in function.
- Nervous system:
- It consists of brain, paired cerebral, pleural, pedal, stellate and visceral ganglia that are joined by nerve connectives and commisures.
- Reproduction:
- Sexes are generally separate, but some are hermaphrodite.
- Reproduction takes place sexually and development may be direct or indirect.
- Larva can be velliger, trochophore or
Classification:
Phylum Mollusca has been divided into following six classes on the basis of foot, shell and mantle.
Class: Monoplacophora
- They are marine.
- Body is segmented and bilaterally symmetrical.
- Foot is flat and ventral.
- Shell consists of single piece or valve.
- Head is without eyes and tentacles.
- Mantle is present which encircles the body as a circular fold of the body wall.
- e.g. Neoplina (connecting link between Annelida and Mollusca).
Class: Aamphineura
- They are mostly marine.
- Body is elliptical, convex dorsally and flattened ventrally.
- Foot is flat and ventral.
- Shell consists of 8 plates.
- Head is distinct but without eyes and tentacles.
- Development is indirect with trochophore larva.
- Mantle is present.
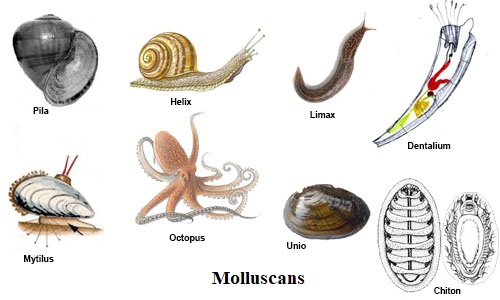
- e.g. Chiton
Class: Scaphopoda
- They are marine.
- Body is elongated and enclosed in a tusk like shell.
- Foot is conical for digging.
- Shell is cylindrical and the head bears a mouth.
- Development is indirect with a trochophore
- Mantle is single lobed and tubular.
- e.g. Dentalium
Class: Gastropoda
- They are either aquatic or terrestrial.
- Body is unsegmented and asymmetrical.
- Foot is sole like, broad, flat and muscular.
- Shell is univalve, hence also called Univalvia.
- Head is distinct with tentacles, eyes and mouth.
- Development is indirect with dorsally located or velliger
- Mantle helps in respiration.
- e.g. Helix (Snail), Limax (Slug), Pila (Apple snail)
Class: Pelecypoda
- Body is laterally compressed.
- The foot is tongue
- Shell is bi-valve and hence also called Bivalvia.
- Head is not distinct.
- Development is indirect with glochidium
- Mantle is paired and consists of right and left lobes.
- They are commonly called pearl forming groups that is secreted by the shell gland of mantle.
- e.g. Unio, Oyster
Class: Cephalopoda
- They are mostly marine.
- Body is bilaterally symmetrical with head and trunk.
- Foot is modified into arms and siphon.
- Foot is situated on the head.
- Shell is absent or internal.
- Head bears large eyes (resembles with that of vertebrates) and mouth.
- Circulatory system is closed type.
- Mantle may be present or absent.
- Development is direct.
- e.g. Sepia, Octopus, Loligo