General characteristics of plants:
- This kingdom includes autotrophic (some are heterotrophic), eukaryotic and multicellular organisms (some are however, unicellular like Cholerlla, Chlamydomonas)
- They live in a wide range of habitats (on land, sea shores and in fresh water).
- Chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoids are usually present in them.
- The reserve food material is starch and fats.
- Cells have a large central vacuole and rigid cell walls composed of cellulose.
- Algae (Spirogyra), bryophytes (moss), pteridophytes (fern), gymnosperms (pine) and flowering plants (angiosperms) are different groups of plants in this kingdom.
The plant kingdom is divided into different divisions (Thallophyta, Bryophyta and Tracheophyta) on the basis of structure of plant body, vascular bundles etc.
In the 2 kingdoms classification system, all the non-flowering plants were kept in a sub-kingdom named Cryptogams. Followings are the non-flowering groups of plants.
- Thallophyta (Algae):
- They are predominantly aquatic, occur bot in marine as well as in fresh water habitats.
- The plant body is a thallus (aggregate of cells with no fixed number), i.e. not differentiated into any prominent structures like root, stem or leaves.
- Their body is generally coated by a layer of mucilage which protects them from dessication (drying) when exposed to air.
- The vascular tissues for water conduction are absent as the entire thallus remain in contact with water.
- Mechanical tissues like the wood of the land plants are also absent in algae.
- Photosynthetic pigments present in algae are chlorophyll a, carotenoids and xanthophylls.
- They reproduce by vegetative, asexual and sexual methods.
- This division is characterized by the absence of embryo stage.
- Green algae (Chloropyta), brown algae (Phaeophyta) and red algae (Rhodophyta) are different types of algae.
E.g. Chlorophyta :- Spirogyra, Volvox, Chlamydomonas, Ulothrix etc.
Phaeophyta :- Fucus, Laminaria, Ectocarpus etc.
Rhodophyta :- Porphyra, Gelidium etc.


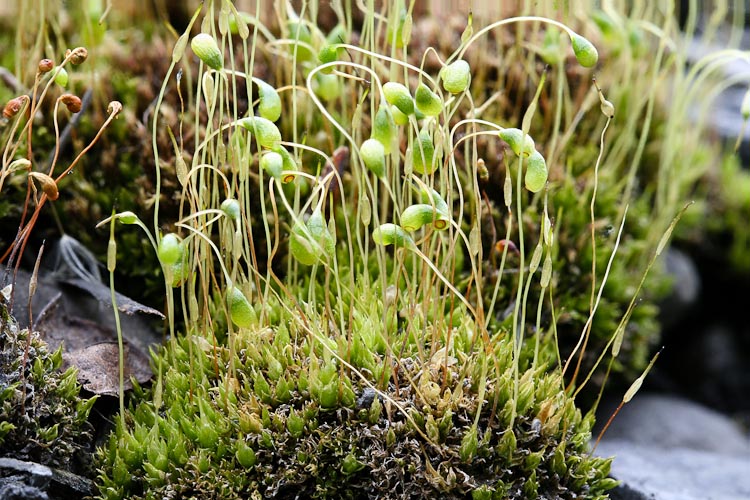
- Bryophyta:
- They usually grow in moist and shady places.
- Bryophytes are fundamentally terrestrial plants but require presence of water to complete their life cycle, hence are also referred to as ‘the amphibian plants’.
- There is alternation of generation in their life cycle, i.e. consists of two distinct phases:
- Gametophytic phase (haploid, dominant, long-lived green and independent).
- Sporophytic phase (diploid, short-lived and dependent on the gametophyte).
- The gametophytes (adult plant) are either thalloid (i.e. differentiated into true roots, stem and leaves) or leafy shoot having stem-like central axis and leaf-like appendages.
- The roots are completely absent or replaced by unicellular or multicellular thread like rhizoids.
- Vegetative reproduction occurs by fragmentation, formation of gemmae and the sexual reproduction is oogamous (i.e. involvement of sperms and eggs).
- Moss (Funaria), liverworts like Riccia, Marchantia etc.


- Tracheophyta:
- These are vascular flowering and non-flowering plants.
- Vascular tissues called xylem and phloem area developed.
- This division is further divided into 3 sub-divisions as follows:
- Pteridophyta
- Gymnosperms
- Angiosperms
Pteridophyta:
- These are the plants with feather like leaves and form the largest group of primitive vascular plants.
- They mostly grow on moist and damp shady places.
- There is alternation of generation in their life cycle (gametophyte and sporophyte are independent of each other unlike in bryophytes).
- The main independent plant body is a sporophyte and is differentiated into true roots, stem and leaves.
- All the vegetative parts possess vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) organized in definite groups.
- The sporangia are either borne singly or in groups called sori and the spores germinate to produce a haploid gametophyte, called prothalus.
- Fertilization occurs in presence of water (i.e. they too are amphibian plants like bryophytes) and the embryo is formed after fertilization.
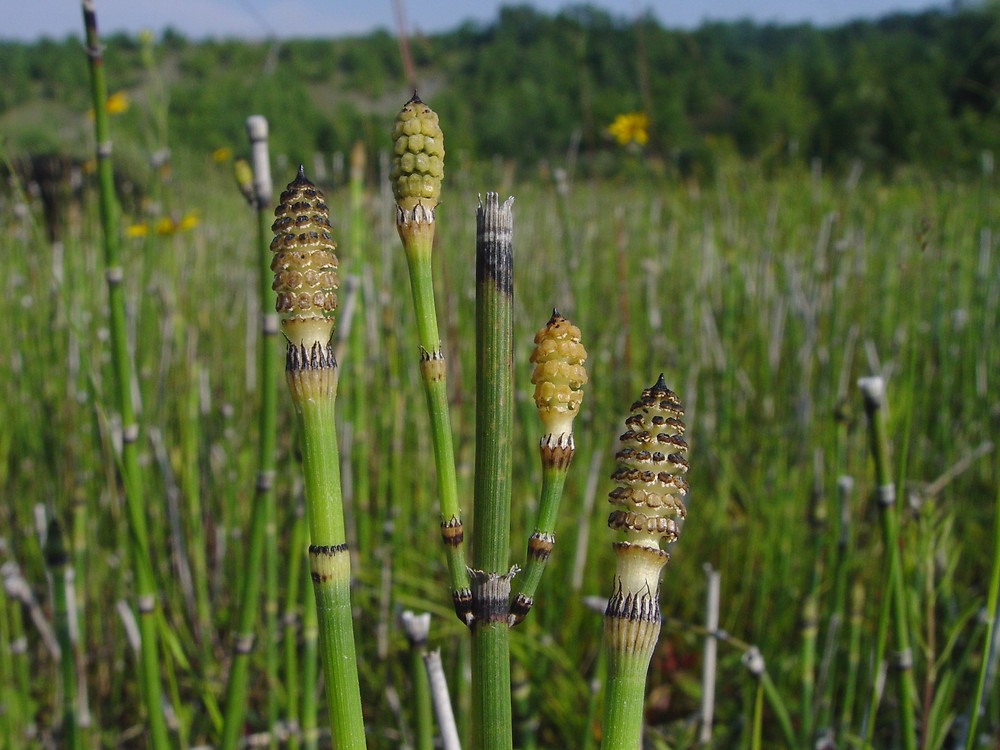
- Ferns (Dryopteris, Pteridium), horsetail (Equisetum), Lycopodium etc.

