- Muscles constitute about 40% of our body weight.
- Muscular tissue helps in movements of the body parts coordinating with the nervous system and skeletal system.
- The study of muscles is known as myology.
- Muscular tissue is mesodermal in origin (except around mammary glands and iris of the eyes).
- Myofibrils are present in muscle fibers.
- Myofibrils contain ATP (Adenosine tri-phosphate), and two proteins Actin and Myosin.
- Muscle cell consists of cytoplasm known as Sarcoplasm and its cell membrane is called Sarcolemma.
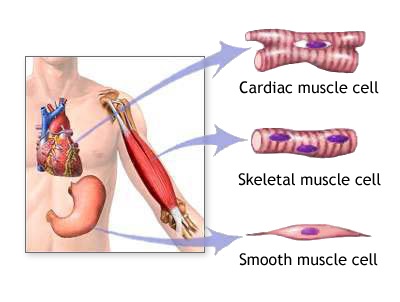
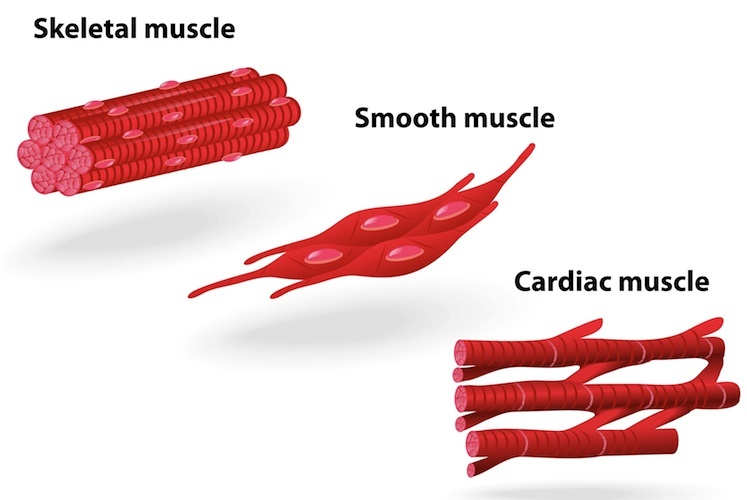
- Muscular tissue is of following 3 types:
1. Striped or striated muscles:
- These muscle fibers are cylindrical and each cell consists of one or more nuclei.
- They are attached to the bones hence also known as skeletal muscles.
- They are also called voluntary muscles they are under the control of our will.
- Myofibrils possess alternate dark and light band, hence appears striped or striated.
- Dark band is called A-band and the light band is called I-band.
- Only actin filaments are present in I-band whereas both actin and myosin filaments are present in A-band.
- In the center of the I-band, a dark Z-line (Krause’s membrane) is present on either side of which actin filaments are attached.
- In the center of A-band, a white H-line (Hensen’s disc) is present where only myosin filaments are present.
- The portion of myofibrils between two Z-lines is called a sarcomere.
- Striped muscles get tired or fatigued and hence require rest between their contractions.
2. Smooth or unstriped muscles:
- There are smaller than striped muscles.
- They are spindle shaped and are uninucleated.
- Sarcoplasm consists of fine granules.
- They don’t contain any bands.
- They are also known as visceral muscles since they are present in walls of visceral organs like stomach, intestinal walls etc.
- They are also called involuntary muscles as they are not under the control of our will.
3. Cardiac muscles:
- They are intermediate between striped and unstriped.
- They are present in the wall of the heart; hence the heart is a myocardium.
- Each muscle fiber has a single nucleus but sarcolemma is absent.
- They are restless and involuntary.
- Contraction and relaxation of such muscle is rhythmic.
Functions of muscles:
- Mobility: The muscles provide mobility to our body or help in body movements for activities like walking, running, swimming, writing etc.
- Stability: Muscle tendons stretching over joints contribute to provide stability in joints and the core muscles in the abdomen, back, and pelvis, stabilize the body and assist in tasks, such as lifting weights.
- Posture: Muscles also help in maintaining correct position and posture of our body during sitting or standing.
- Vision: Six skeletal muscles around the eye control its movements and also help to scan the surrounding area, maintain a stable image and track moving objects.
- Circulation: The heart muscle (cardiac muscle) pumps blood thus helps in circulation of blood.
- Breathing: The muscles present in the lungs and the strong muscular structure called diaphragm help in contraction and relaxation of lungs thus aiding n breathing.
- Digestion: Movement of smooth muscle in GI tract that causes peristalsis help in proper digestion of food.
- Urination: The muscles and nerves work together to hold and release urine from the bladder.