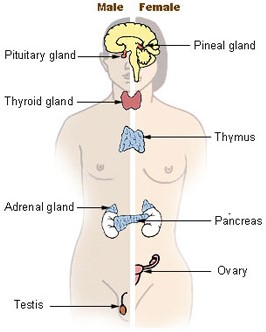
- Gonads:
- Gonads are the organs that produce gametes.
- One pair of ovaries (in females) and a pair of testes (in males) are the gonads that also secrete hormones to regulate the reproductive functions.
- These hormones (also called sex hormones) include the male androgens and the female estrogens, progestins (progesterone) and relaxin.
Male sex hormones:
- The interstitial cells (Leydig cells) of testes produce testosterone.
- Testosterone acts with luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) secreted by adenohypophysis to stimulate spermatogenesis.
- Spermatogenesis is the process of formation of sperms in testes.
- Testosterone is also necessary for the growth and maintenance of the male sex organs.
- It also promotes the development of the sexual behavior and male secondary sexual characteristics like:
- Growth and development of facial and pubic hair.
- Enlargement of larynx that causes the voice to deepen.
- Development of abdominal muscles and V-shaped body etc.
- The testes also produce the hormone called inhibin, which inhibits the secretion of FSH by pituitary gland.
Female sex hormones:
- Three major classes of ovarian hormones help regulate female reproductive functioning.
- Like in testes, the secretions of ovaries are also regulated by FSH and LH from the anterior lobe of pituitary gland.
- Estrogens help regulate the menstrual cycle and the development of mammary glands.
- They also help in the development of female secondary sexual characteristics like:
- High pitched voice.
- Less pronounced body hair (mostly in pubic region).
- Wider hips (for child bearing) etc.
- Progesterone also regulates the menstrual cycle, development of mammary glands and aids in the formation of placenta (the organ in the uterus for nourishing the developing baby and removing the waste) during pregnancy.
- It also inhibits the secretion of FSH.
- Relaxin is involved in childbirth, which softens the cervix of the uterus at the time of delivery and also causing the relaxation of ligaments of the pubic symphysis.

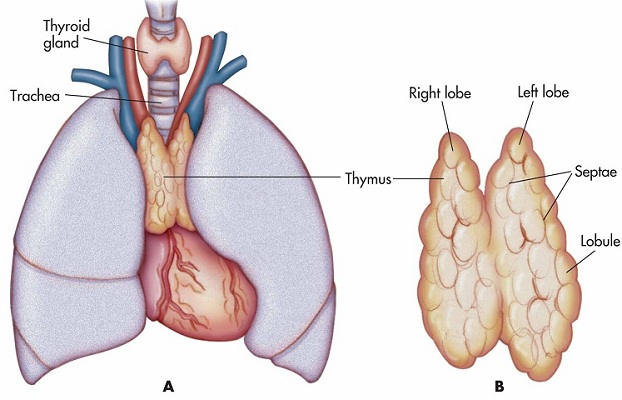
- Thymus gland:
- It is a bilobed and flattened gland located just in front of the heart.
- It is active in young people (during adolescence) and becomes inactive with age after puberty.
- The gland is divided into two parts; outer cortex and inner medulla.
- Cortex consists of thymocytes and more lymphocytes whereas medulla has less lymphocytes and cluster of cells called Hassall’s corpuscles.
- Thymus gland is well supplied with blood vessels but has only a few nerve fibers.
- It helps in the maturation of T-cells (T- lymphocytes) and hence is called the training school of T-cells.
- These T-cells help in the development of cellular immunity in our body.
- Thymosin hormone secreted from this gland before puberty is thought to control growth and maturity in people.
- Pineal gland:
- It is a pea-sized gland found near the diencephalon of brain.
- This gland converts the signal of light and dark received from the nervous system (optic nerve) into the endocrine signal, hence also referred to as a third eye.
- Hormone melatonin secreted by this gland regulates the development of gonads and slows menstrual cycle in females.
- It also works in antagonism with melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH) to make our skin lighter in color.

- Digestive system:
- Gastrin, Secretin and Cholecystokinin are major hormones secreted by the mucosal cells present in the digestive tract.
- Gastrin (secreted by the walls of stomach) stimulates the production of HCl and the digestive enzyme (pepsin) when the food enters the stomach.
- Secretin (secreted by the mucosa of duodenum) stimulates a bicarbonate rich secretion from the pancreas that neutralizes stomach acid as the acid passes to the small intestine.
- Cholecystokinin (secreted by the mucosa of duodenum) stimulates the contraction of gall bladder, which releases bile when food (particularly fats) enters the duodenum.
- Placenta:
- It is a specialized organ that develops in a pregnant female in her uterus.
- It acts as a source of nourishment and oxygen for the developing fetus.
- Estrogen, progesterone and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which help maintain pregnancy are produced by placenta.
- Target areas for these hormones are the ovaries, mammary glands and uterus.