General features of flowering plants
- Previously, all the flowering plants were kept in the sub-kingdom called Phanerogams.
- They are the most developed and economically important plants.
- All flowering plants bear seeds and are hence also known as spermatophytes.
- These plants have distinct roots, stem, leaves and flowers.
- The vascular system is also well developed in these plants.
- Division Tracheophyta consists of three sub-divisions; Pteridophyta (a non-flowering division), and the two flowering divisions, Gymnospermae and Angiospermae.
- Gymnospermae:
- Commonly known as conifers, they produce woody cones which are fruits made up of scales.
- They bear seeds but without a seed coat. i.e. ovules are not enclosed within an ovary and the seed is naked.
- They are distributed in the cold climates where snow, rather than rain, is the source of water.
- They are mostly perennials, xerophytic, evergreen and tall woody plants.
- They bear unisexual cones, i.e male and female cones are found in different branches of the same plant or different plants.
- Pollination usually takes place with the help of wind.
- The vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral and open.
- The wood is usually soft and is widely used for lumber and timber.
- e.g. Cycas, Pinus, Fir, Larch etc.

- Angiospermae:
- The most dominant ubiquitous flowering plants belong to this sub-division.
- Flowers are well developed and bear ovules inside the ovary; hence the seeds are enclosed within the fruit.
- The flower normally consists of four whorls; calyx (sepals), corolla (petals), androecium (stamens) and gynoecium (pistil).
- Most of them are bisexual and few are unisexual.
- Insects and animals usually act as pollinating agents as the petals are attractive.
- They may be herbs, shrubs or trees.
- e.g. peepal, orange, apple, maize, rice etc.
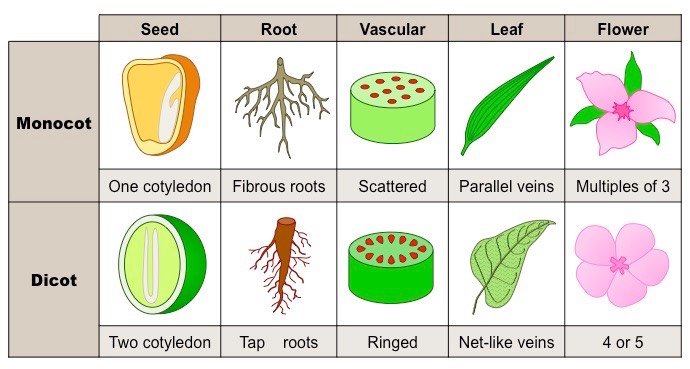
The sub-division Angiospermae is further divided into two classes; Monocotyledonae and Dicotyledonae.
Monocotyledonae:
- These plants have only one seed leaf (cotyledon) in their seeds.
- They have long and narrow leaves with parallel venation.
- They have a fibrous or adventitious root system.
- They are mainly herbs (stem is hollow, herbaceous and soft).
- Nodes and internodes are present on stem and can be easily broken at these points.
- Stem consists of open and scattered vascular bundles and lack vascular cambium.
- The number of petals is either three (trimerous) or multiple of three.
- e.g. rice, wheat, maize, onion, lily, Pistia, Lemna, sugarcane, bamboo etc.
Dicotyledonae:
- These plants have two seed leaves (cotyledons) in their seeds.
- The leaves are either simple or compound and are broad with net like reticulate venation.
- They have tap root system with secondary roots.
- They are ubiquitous and are herbs, shrubs or trees.
- The stem is normally solid, hard and woody with no nodes and internodes.
- Vascular bundles are closed and arranged in a ring.
- The flower usually bears four or five petals or their multiples.
- e.g. gram, pea, mustard, apple, mango, sunflower etc.