| S.N. |
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) |
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) |
| 1. |
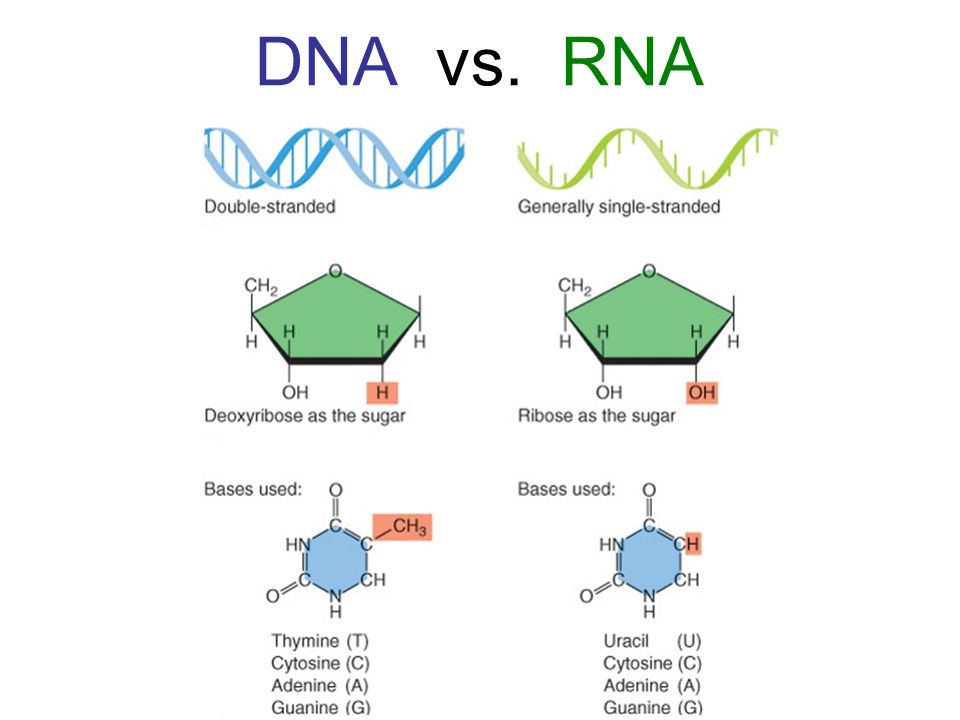
It contains ribose sugar. |
It contains deoxyribose sugar. |
| 2. |
It lacks Thymine but has Uracil. |
It lacks Uracil but has Thymine. |
| 3. |
It is a single chain of polynucleotides. |
It is a double chain of polynucleotides. |
| 4. |
The quantity of RNA varies in different cells. |
The quantity of DNA is fixed in each cell of a species, except gametes. |
| 5. |
It mainly occurs in the cytoplasm with small quantity found in the nucleus. |
It mainly occurs in the nucleus with small quantity found in mitochondria and plastids. |
| 6. |
It is formed by DNA and cannot replicate itself. |
It can replicate itself. |
| 7. |
RNA is the main component of ribosomes. |
DNA is the main component of chromosomes. |
| 8. |
It guides protein synthesis and also guides the replication process. |
It controls structure, metabolism, differentiation, heredity and evolution. |
| 9. |
It is of 3 main types; mRNA (messenger RNA), tRNA (transfer RNA) and rRNA (ribosomal RNA). |
It is of 2 types; linear intranuclear and circular extranuclear. |
| 10. |
RNA molecule is relatively short (70-12000 nucleotides) and has a relatively low molecular weight. |
DNA molecule is very long (millions of nucleotide pairs) and the molecular weight is very high. |
| 11. |
No primer is needed for the transcription of RNA. |
A primer is needed for the replication of DNA. |
| 12. |
It is hydrolyzed by the enzyme RNase (ribonuclease). |
It is hydrolyzed by the enzyme DNase (deoxyribonuclease). |
| 13. |
The mRNA translates its information into polypeptides. |
DNA transcribes its genetic information to mRNA. |
| 14. |
RNA doesn’t show helical coiling. |
DNA shows a double helical coiled structure. |
| 15. |
It is genetic material in certain viruses. |
It is a genetic material in all organisms. |