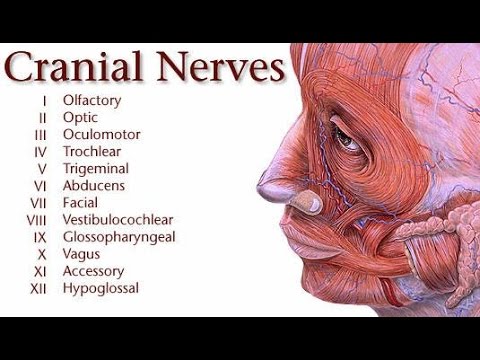
- The nerves that arise from the brain and supply to the head, neck and face are called cranial nerves.
- There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves which are the parts of peripheral nervous system.
- Their names are an indication of some of their anatomical or functional features, and their numbers (Roman numerals) indicate the sequential order in which they emerge from the brain.
- Cranial nerves I and II are nerves of the cerebrum, nerves III to XII are nerves of the brainstem (XI partly emerging from spinal cord).
- Of the 10 brainstem nerves, 1 (VIII) is a purely sensory nerve, 5 (III,IV,VI,XI and XII) are primarily motor nerves and 4 (V,VII,IX and X) are mixed nerves, i.e. containing both sensory and motor fibers.
- The cranial nerves are generally concerned with the specialized (special) senses of smell, taste, vision, hearing and balance, and with the general senses.
- They are also involved with the specialized motor activities of eye movement, chewing and swallowing, breathing, speaking and facial expression.
- The 12 pairs of cranial nerves are as follows:
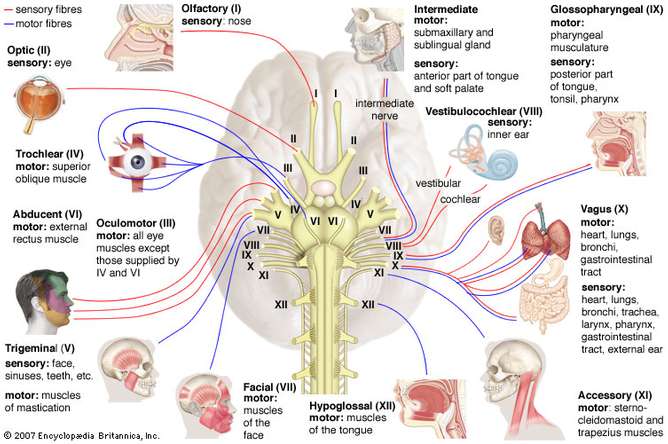
Cranial nerve I (Olfactory nerve):
- Type: sensory nerve
- Origin: nasal mucous membrane high in the nasal cavities.
- Distribution: terminates in the olfactory bulb of cerebrum
- Function: perception of smell or olfaction
Cranial nerve II (Optic nerve):
- Type: sensory nerve
- Origin: retina of the eye
- Distribution: terminates in lateral geniculate body of thalamus and superior colliculus of midbrain
- Function:
- perception of vision
- adjusts lens and constricts pupil helping in the reflex of focusing
Cranial nerve III (Oculomotor nerve):
- Type: motor nerve
- Origin: midbrain
- Distribution:
- to all extrinsic muscles of eyeball except superior oblique and lateral rectus
- in the autonomic fibers to ciliary muscles of lens and constrictor muscle of iris
- Function:
- movements of eyeball, elevation of upper eyelid
- constriction of pupil
- accommodation of the lens (focusing by the lens)
Cranial nerve IV (Trochlear nerve):
- Type: motor nerve
- Origin: caudal midbrain
- Distribution: innervates special oblique muscles of eye
- Function: eye movements (down and out)
Cranial nerve V ( Trigeminal nerve):
- This nerve consists of three major branches and is the largest cranial nerve.
- It is a mixed nerve, sensory nerve of the face, oral and nasal regions, and motor nerve of the chewing muscles.
- The ophthalmic nerve (V1):
- Sensory nerve
- Originates and supplies to the general area of forehead and eyes
- It conveys general senses from cornea of eyeball, upper nasal cavity, front of scalp, forehead, upper eyelid, conjunctiva and lacrimal (tear) glands.
- The maxillary nerve (V2):
- Sensory nerve
- Originates and supplies to the general area of maxillary region
- Conveys general senses from cheek, upper lip, upper teeth, mucosa of nasal cavity, palate and parts of pharynx
- The mandibular nerve (V3):
- Mixed nerve (both sensory and motor)
- Sensory branch originates and supplies to the general area of mandibular region
- It conveys general senses from tongue (not taste), lower teeth and skin of lower jaw
- Motor branch originates in the pons and supplies to the muscles of mastication
- It helps in chewing
Cranial nerve VI (Abducens nerve):
- Type: motor nerve
- Origin: caudal pons
- Distribution: innervates the lateral rectus muscle of eye
- Function: helps in the abduction of the eye, i.e. lateral movements of the eye
Cranial nerve VII (Facial nerve):
- Type: mixed nerve
- Origin: pons
- Distribution and function:
- sensory branch innervates the taste buds of tongue and helps in the perception of taste of food
- motor branch innervates the muscles of facial expression, autonomic fibers to salivary glands, and lacrimal glands
- it helps in salivation, lacrimation (tear production), movement of muscles of facial expression
Cranial nerve VIII (Vestibulocochlear nerve):
- It is a sensory nerve composed of two nerves; the cochlear nerve and the vestibular nerve
1. The cochlear nerve:
- Sensory nerve
- Originates and supplies to the cochlea of inner ear
- It helps in the perception of hearing
2.The vestibular nerve:
- Sensory nerve
- Originates and supplies to the semicircular ducts, utricle and saccule of inner ear
- It helps in maintaining the body balance or equilibrium.
Cranial nerve IX (Glossopharyngeal nerve):
- Type: mixed nerve
- Origin: medulla oblongata
- Distribution and function:
- Sensory branch originates and supplies to the posterior third of tongue and upper pharynx
- It helps in the perception of taste and other sensations of the tongue along with general senses from upper pharynx
- Motor branch originates and supplies to the stylopharyngeus muscle and autonomic fibers of parotid gland.
- It helps in the secretion of saliva and swallowing of food.
Cranial nerve X (Vagus nerve):
- Type: mixed nerve
- Origin: medulla oblongata
- Distribution: innervates the voluntary muscles of soft palate, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle in respiratory, cardiovascular and digestive system
- Function:
- helps in swallowing
- monitors the oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations in blood
- Senses blood pressure and other visceral activities of affected systems.
Cranial nerve XI (Accessory nerve):
- Type: it is a spinal accessory nerve and is a motor nerve
- Origin: medulla oblongata and cervical spinal cord
- Distribution: muscles of larynx, strenocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
- Function: voice production from larynx, muscle sense, and movement of the head and shoulders
Cranial nerve XII (Hypoglossal nerve):
- Type: motor nerve
- Origin: medulla oblongata
- Distribution: innervates the tongue muscles
- Function: movements of tongue during speech, helps in swallowing and muscle sense
thank you sir.
keep up the good work.