- This family is commonly known as Lily family.
- These plants are normally grown or cultivated for vegetable purpose.
- The plants are found in temperate and tropical regions. They are perennial with pungent flower due to the presence of sulfur compound.
- They are normally herbs or shrubs and rarely trees.
Roots: The roots are normally adventitious or fibrous but may be tuberous as in case of Asparagus.
Stem:
- The stem is aerial or underground, erect, reduced and weak.
- Underground stem is fleshy (e.g. corms), rhizomes (e.g. Gloriosa), bulbs (eg. Onions, garlic) etc.
- In some cases, the branches are modified into green, leaf like flattened structures called phylloclades or cladodes.
Leaves:
- Leaves are radical, ramal or cauline and alternate.
- They are hollow, simple, sessile and
- Foliage leaves are absent and replaced by scale leaves in some cases.
- The bases of foliage leaves are fleshy, non-green and overlapping to form a bulb like structure in onion.
- Leaves are with parallel venation in most plants but Smilax has reticulate venation.
Inflorescence:
- Aggregation of many monochasial cyme in umbellate form and borne on a leafless scape.
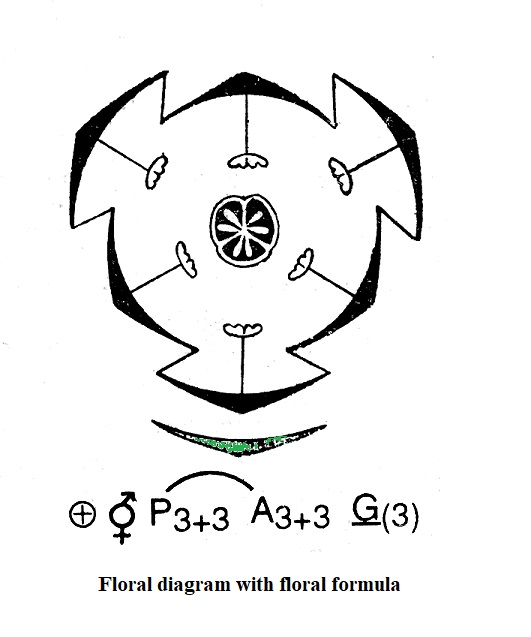
Flowers:
- Bracteate or ebracteate, incomplete or complete, bisexual or unisexual
- Pedicellate, hypogynous, actinomorphic, trimerous
- The flowers are generally small and white in color.
Perianth:
- Six tepals are arranged in two alternating whorls of 3 each.
- Poly- or gamophyllous, petaloid, white with green midrib and are inferior
Androecium:
- Six stamens are present, antipetalous polyandrous and epiphyllous
- Stamens are arranged opposite the perianth or tepals.
- Filament long but slightly dilated at the base
- Anther is long, bilobed and basifixed.
Gynoecium:
- Tricarpellary syncarpous, ovary is superior and trilocular.
- Axile placentation, style is single and stigma is trilobed and capitate.
Fruit: Capsule or berry
Floral diagram with floral formula (Allium cepa or onion):
Some important plants of the family:
- Allium cepa (onion)
- Allium sativa (garlic)
- Asparagus officinalis (garden asparagus)
- Ruscus aculeatus (butcher’s broom)
- Aloe vera
- Similax ovalifolia (kumarika)
- Gloriosa superba (flame lily)
- Asphodelus tenuifolius (common weed)
- Yucca olaifolia (dagger plant)
Economic importance:
- Allium cepa, Allium sativa, Asparagus officinalis are commonly used as vegetables and for enhancing flavor in vegetables.
- Gloriosa, Asparagus, Ruscus are used for ornamental purpose.
- Smilax, Urginer indica, Asparagus are used as medicinal plants.
- Yucca and Agave are used to yield fibers. The fibers are taken out from the leaves.
- Lilium is an annual herb cultivated in gardens for ornamental purpose.