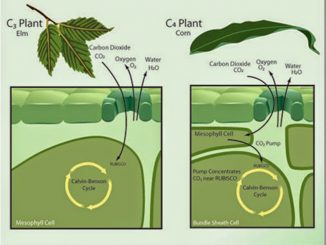
Differences between C3 and C4 cycles
S.N. Calvin cycle (C3 cycle) Hatch and Slack cycle (C4 cycle) 1. The primary acceptor of CO2 is a 5-carbon compound, Ribulose-1, 5- biphosphate. The […]

S.N. Calvin cycle (C3 cycle) Hatch and Slack cycle (C4 cycle) 1. The primary acceptor of CO2 is a 5-carbon compound, Ribulose-1, 5- biphosphate. The […]

When the primary root, which is a direct prolongation of the radicle, remains distinct throughout the life of the plant and gives off lateral branches, […]
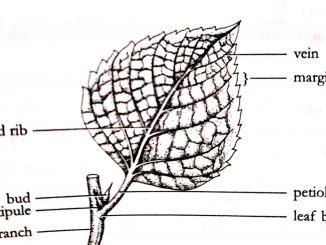
The leaf is a flattened lateral out-growth of the stem/ branch and bears a bud in its axil. It is green in color due to […]
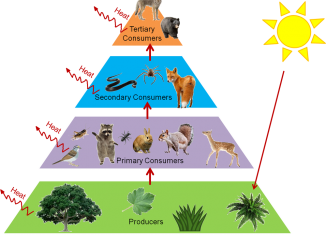
In an ecosystem, green plants act as producers and the food prepared by green plants is consumed by a series of consumers. In a food […]
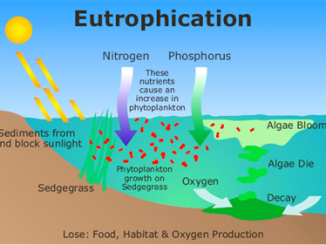
Eutrophication is derived from the Greek word ‘eutrophos’ that means well-nourished or enriched Eutrophication is the excessive presence of nutrients like nitrate and phosphate in […]
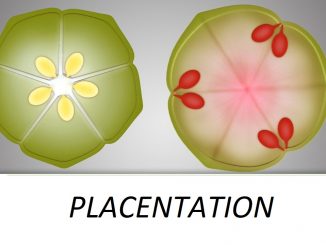
Ovary is the most important part of the carpel as it contains ovules that develop into seeds after fertilization. The ovary may consist of different […]
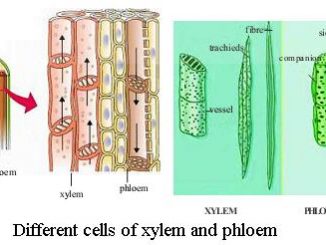
A group of more than one type of cells having common origin and performing different but closely related functions as a unit is called complex […]
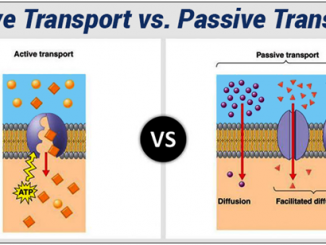
S.N. Active Transport Passive Transport (Diffusion) 1. The materials move through a bio-membrane against the concentration gradient or electrochemical gradient. The materials move across a […]
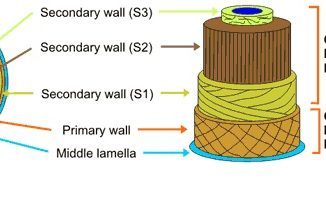
S.N. Primary cell wall Secondary cell wall 1. It is formed in a growing cell. It is formed in a mature cell. 2. It lies […]
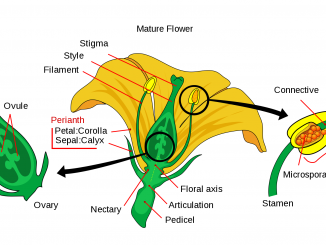
Flowering plants are kept in the group phanerogams. They are also known as spermatophytes as they produce seeds. In higher angiosperms, the flowers are produced […]
Copyright © 2025 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes