
Benedict’s Test: Principle, Requirements, Procedure and Result Interpretation
A sugar consists of an anomeric carbon to which a functional group is attached. If the anomeric carbon consists of aldehyde as a functional group, […]

A sugar consists of an anomeric carbon to which a functional group is attached. If the anomeric carbon consists of aldehyde as a functional group, […]

A compound in which a metal atom or ion is co-ordinated to two or more anions or neutral molecules is called co-ordination or complex compound. […]
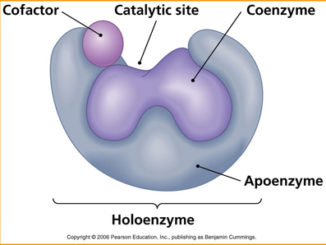
Except for a small group of RNA molecules that act as catalyst, all enzymes are proteins. Catalytic activity of enzymes depends on the integrity of […]
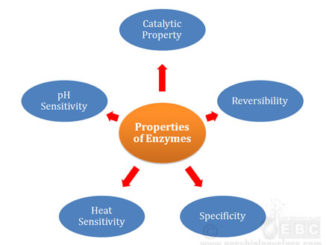
Enzymes are organic compounds (mostly proteins) produced by the living cells to speed up the spontaneous biochemical reactions in and outside the cells in living […]

The Fehling test was developed in 1848 by Herrmann Fehling. Like Benedict’s test, it is also a sensitive test for the detection of reducing sugars. […]
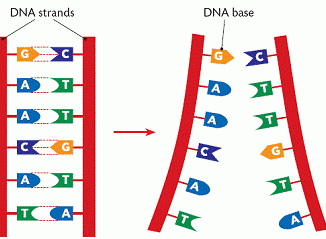
Nucleic acids are the components of our nuclear material (Chromosomes) present in the cells. Nucleic acids are also ingested from food like herring, mackerel etc. […]

Amino acids are the fundamental units of protein or polypeptides. They are organic compounds having two functional groups; one acidic carboxylic (-COOH) group and the […]

Biuret is a compound formed by heating urea at 1800 It is the result of the condensation of 2 molecules of urea. The peptide bonds […]
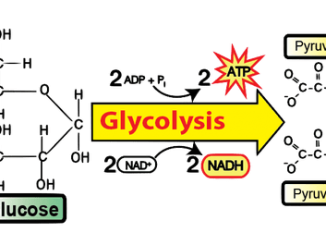
All the living organisms whether aerobes or anaerobes, initiate the mechanism of respiration by breaking down glucose (6 carbon compound) into two molecules of pyruvate […]
Copyright © 2025 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes