
- Bacitracin test is one of the antimicrobial disc tests used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria to bacitracin.
- It is used for distinguishing group A β-hemolytic Streptococci from other β-hemolytic Streptococci. It also distinguishes Staphylococci sps.(resistant) from micrococci (susceptible).
Principle:
- Bacitracin test is used to determine the effect of a small amount (0.04U) of bacitracin on an organism.
- A disk infused with bacitracin is placed on an agar plate inoculated with organisms.
- The antibiotic diffuses into the medium and inhibits the growth of susceptible organisms.
- Bacitracin is a polypeptide antibiotic that is obtained from Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus subtilis etc.
- The synthesis of peptidoglycan component of bacterial cell wall is interfered by bacitracin as it blocks bactoprenol from transporting NAM and NAG sugars across the cell membrane, thereby inhibiting the further synthesis of peptidoglycan.
- After complete incubation, the inoculated plates are observed for zones of inhibition around the disks.
- Any zone of inhibition around the disk suggests the organism has not grown and is sensitive to bacitracin whereas if the organism grows up to the edge of the disk, it is resistant to the bacitracin infused in the disk.
Requirements:
- Test organisms
- Control organisms
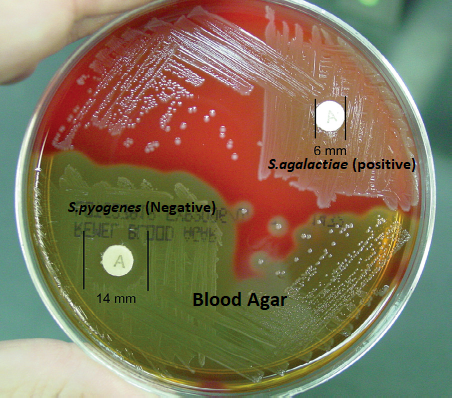
- Positive: Streptococcus pyogenes
- Negative: Streptococcus agalactiae
- Blood agar (trypticase soy agar + 5% sheep blood)
- Sterile forceps
- Inoculating loops
- Incubator
- Disc infused with bacitracin(0.04U)
Procedure:
- 2-3 isolated colonies from pure culture are selected with a sterile inoculating loop.
- The colonies are streaked on different sections of a blood agar plate resulting in lawn culture. Using sterile forceps, a bacitracin disc is placed gently on the area with dense growth.
- The disk was gently tapped to ensure appropriate contact with the agar surface.
- The inoculated plate was incubated at 35-37oC for 18 to 24 hours in ambient air.
- The plate was observed for zone of inhibition around the disc.
Result interpretation:
- Positive test:
- Any zone of inhibition more than 10mm around the disc suggests positive result. i. e. organism is susceptible to Bacitracin.
- E.g. Beta-hemolytic streptococci (Streptococcus pyogenes), Micrococcus
- Negative test:
- No zone of inhibition around the disc indicates negative result. i.e. organism is resistant to Bacitracin.
- E. g. Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus
https://histogene.ir/bacitracin-susceptibility-test/
Limitations:
- The diffusion of antibiotics on old blood agar plates is reduced and might show false-negative results if used.
- Different zone of inhibition sizes might be observed with different concentrations of Bacitracin; thus, differential disks (0.04 U) should be used instead of sensitivity disks (10 U).
- Sufficient inoculum should be used that results in confluent growth because light inoculum might result in a false zone of inhibition.
- It isn’t used for complete identification of organisms. Hence, different biochemical and/or serological tests such as latex agglutination are recommended for complete identification.