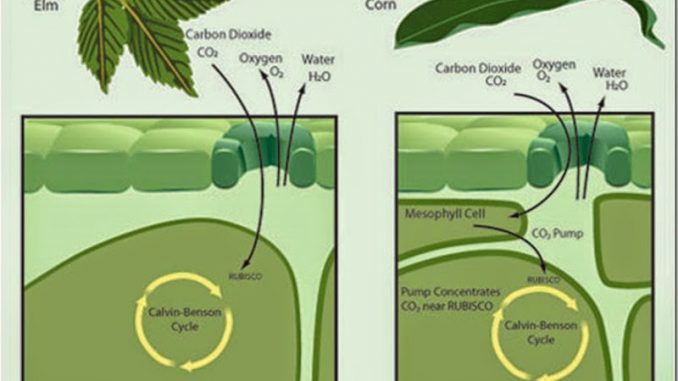
| S.N. | Calvin cycle (C3 cycle) | Hatch and Slack cycle (C4 cycle) |
| 1. | The primary acceptor of CO2 is a 5-carbon compound, Ribulose-1, 5- biphosphate. | The primary acceptor of CO2 is a 3-carbon compound, phosphoenol pyruvic acid. |
| 2. | The first stable compound is a 3-carbon compound, phosphoglyceric acid. | The first stable compound is a 4-carbon compound, oxaloacetic acid. |
| 3. | Chloroplasts are monomorphic (only one type). | Chloroplasts are dimorphic (two types of chloroplasts); the mesophyll chloroplasts perform C4 cycle and bundle sheath chloroplasts perform C3 cycle. |
| 4. | Leaves don’t show Kranz anatomy. | Leaves show Kranz anatomy. |
| 5. | Photorespiration occurs in C3 plants. | Photorespiration rarely occurs. |
| 6. | It is less efficient in utilizing atmospheric carbon dioxide. | It is much efficient in utilizing atmospheric carbon dioxide (even when stomata are nearly closed.) |
| 7. | Plants are adapted to all climates except for saline conditions (salty conditions). | Plants are adapted to tropical climates and can also tolerate halophytic (salty) conditions. |
| 8. | It is less energy expensive (requires only 18 ATP for the synthesis of one molecule of glucose). | It is more energy expensive and requires 30 ATP for the synthesis of one molecule of glucose. |