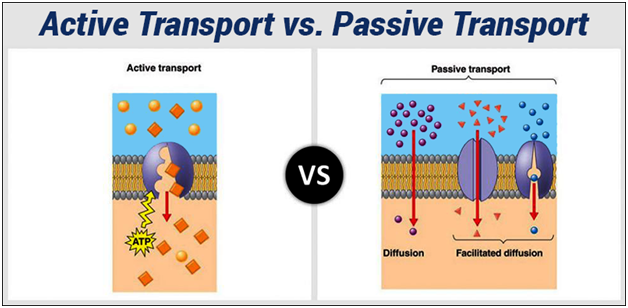
| S.N. |
Active Transport |
Passive Transport (Diffusion) |
| 1. |
The materials move through a bio-membrane against the concentration gradient or electrochemical gradient. |
The materials move across a bio-membrane along or down the concentration gradient or electrochemical gradient. |
| 2.
|
Carrier molecules are needed for this process. |
It generally occurs without the help of carrier molecules but facilitated diffusion needs assistance from membrane proteins, such as channels and carriers. |
| 3. |
Molecules move actively from the region of their lower concentration to the region of their higher concentration. |
Molecules move passively from the region of their higher concentration to the region of their lower concentration. |
| 4. |
It uses energy of ATP or the movement of ions down a gradient across a membrane. |
No energy is used for this process. |
| 5. |
It takes place in one direction only (unidirectional process). |
It takes place in both the directions.
|
| 6. |
It is affected by the oxygen supply, temperature and toxins (poisons). |
It is not affected by oxygen, temperature and toxins. |
| 7. |
It is a rapid or fast process. |
It is a slow process. |
| 8. |
It brings about selective uptake of materials like proteins, ions and complex sugars. |
It allows all transmissible molecules like water, oxygen,CO2, small sugars etc. to pass across membranes. |
| 9. |
It is stopped by metabolic inhibitors. |
It is not influenced by metabolic inhibitors. |
| 10. |
Leads to accumulation of materials in the cells. |
It doesn’t accumulate the materials in the cells. |
| 11. |
It is a vital process, i.e. allows the transportation of nutrients and wastes against the concentration gradient. |
It is one of the normal physical processes which maintains a dynamic equilibrium of water, gases, nutrients and wastes in and out of the cell. |
| 12. |
No equilibrium of molecules is established. |
No net movement of molecules is observed after the establishment of equilibrium on either side of the membrane. |