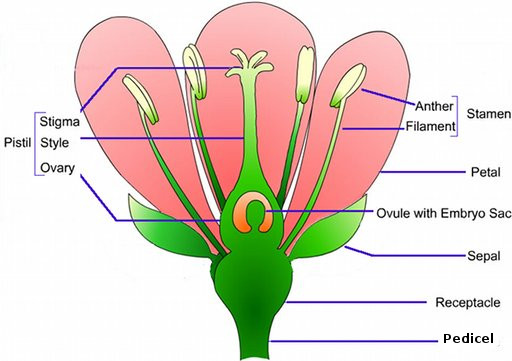
- Flowers are the reproductive organs in Angiosperms. A flower is borne on a stalk called pedicel with an upper swollen region known as thalamus. A typical flower has four whorls, namely: calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium.
- Calyx (the outermost whorl) is formed by a group of leaf-like structures called sepals which enclose the bud and protect it.
- Corolla (the second whorl) consists of number of colorful petals that attract insects for pollination.
- Androecium (the male reproductive organ) is the collection of varying number of stamens. Each stamen consists of filament and anther. Anther produces pollen grains that form male gametes.
- Gynoecium (the innermost whorl) is the female reproductive organ that consists of stigma, style and ovary. The ovary encloses ovules that form female gametes.
- Sexual reproduction in angiosperms involves the formation of gametes in the respective organs followed by pollination and fertilization forming seeds and embryo.
- Formation of gametes:
Male gametes:
- An anther is a bilobed structure that contains 4 pollen sacs.
- Each pollen sac is provided with diploid microspore mother cells.
- Each diploid microspore mother cell forms 4 haploid microspores (pollen grains) by meiosis.
Female gametes:
- Ovary consists of ovules developed from its inner wall.
- An ovule consists of diploid megaspore mother cell.
- A diploid megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to form 4 haploid cells.
- Out of these,3 degenerate and one becomes functional that is a megaspore.
- Each megaspore develops into the embryo sac which consists of 8 cells as follows;
- 3 antipodal cells, 2 synergids, 2 polar nucleus (secondary nucleus or definitive nucleus) and 1 egg cell (female gamete).
- Pollination:
- The process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther of stamen to the stigma of pistil in a flower is called pollination.
- Self-pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower.
- Self-pollination normally occurs in bisexual flowers without the involvement of any external agents like insects, animals, wind or water.
- Cross-pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same plant or different plants.
- Cross-pollination occurs both in unisexual and bisexual flowers with external agents like water, insects etc. needed.
- Fertilization:
- The process of fusion of male and female gametes (male and female nuclei) to form a zygote is called fertilization.
- After pollination, when the pollen grains reach on the stigma, a pollen tube grows down through the style from each pollen grain.
- Pollen grain divides by mitosis inside the pollen tube to form two male gametes.
- The growth of pollen tube through the style finally causes the male gametes to reach the micropyle of the ovule and are released into the embryo sac.
- One male gamete unites with the egg and another one with the secondary nucleus.
- Zygote (diploid) is produced from the fertilized egg whereas the fusion of other male gamete with the secondary nucleus forms the endosperm (triploid).
- Since one pair of male gametes fuse with the egg cell and secondary nucleus respectively, this fertilization in higher angiosperms is called double fertilization.
- Formation of seed and fruit:
- Sepals, petals and stamens all wither and fall off after fertilization.
- The ovule as a whole develops into seeds while the ovary develops into fruit.
- The endosperm nourishes the seeds till they get matured.
- After maturation, the seeds come out of the fruit and form seedlings and finally grow into new plants in suitable conditions.

this is really helpful
thank you 🙂